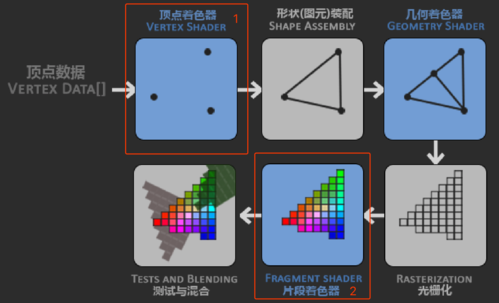
在之前的展示中我们已经创建好了一个正方形,接下来我们要做的就是给它添加一抹色彩。添加颜色可以通过修改着色器来实现。
给顶点着色
在 webgl 中,物体是由一系列顶点组成的,每一个顶点都有位置和颜色信息。在默认情况下,所有像素的颜色(以及它所有的属性,包括位置)都由线性插值计算得来,自动形成平滑的渐变。我们以前的顶点着色器没有给顶点添加任何特定的颜色——在顶点着色器与片段着色器之间给每个像素着白色,于是整个正方形被渲染成纯白。
现在我们假设正方形的每个顶点使用不同的颜色:红,黄,绿,白,以此渲染一个渐变的色彩。第一步,要给这些顶点建立相应的颜色。首先我们要创建一个顶点颜色数组,然后将它们存在 WebGL 的缓冲区中。为实现这一功能,我们在 initBuffers() 函数中加入如下代码:
function initColorBuffer(gl) {
const colors = [
1.0,
1.0,
1.0,
1.0, // 白
1.0,
0.0,
0.0,
1.0, // 红
0.0,
1.0,
0.0,
1.0, // 绿
0.0,
0.0,
1.0,
1.0, // 蓝
];
const colorBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(colors), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
return colorBuffer;
}
这段代码首先建立了一个 JavaScript 的数组,此数组中包含四组四值向量,每一组向量代表一个顶点的颜色。然后,创建一个 WebGL 缓冲区用来存储这些颜色——将数组中的值转换成 WebGL 所规定的浮点型后,存储在该缓冲区中。
当然,我们也需要从 initBuffers() 中调用这个新函数,并返回它创建的新缓冲区。
为了实际使用这些颜色,我们继续修改顶点着色器,使得着色器可以从颜色缓冲区中正确取出颜色:
// Vertex shader program
const vsSource = `
attribute vec4 aVertexPosition;
attribute vec4 aVertexColor;
uniform mat4 uModelViewMatrix;
uniform mat4 uProjectionMatrix;
varying lowp vec4 vColor;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = uProjectionMatrix * uModelViewMatrix * aVertexPosition;
vColor = aVertexColor;
}
`;
与之前相比,这段代码的关键不同点在于:每个顶点都与一个颜色数组中的数值相连接。
给片段着色
为使每个像素都得到插值后的颜色,我们只需要在此从 vColor 变量中获取这个颜色的值:
// Fragment shader program
const fsSource = `
varying lowp vec4 vColor;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vColor;
}
`;
带颜色的绘制
接下来,我们要初始化颜色属性,以便着色器程序使用
// Collect all the info needed to use the shader program.
// Look up which attributes our shader program is using
// for aVertexPosition, aVertexColor and also
// look up uniform locations.
const programInfo = {
program: shaderProgram,
attribLocations: {
vertexPosition: gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, "aVertexPosition"),
vertexColor: gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, "aVertexColor"),
},
uniformLocations: {
projectionMatrix: gl.getUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "uProjectionMatrix"),
modelViewMatrix: gl.getUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "uModelViewMatrix"),
},
};
然后,我们便可以修改 drawScene() 使之在绘制正方形时使用这些颜色:
// draw-scene.js
function setColorAttribute(gl, buffers, programInfo) {
const num***ponents = 4;
const type = gl.FLOAT;
const normalize = false;
const stride = 0;
const offset = 0;
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffers.color);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
programInfo.attribLocations.vertexColor,
num***ponents,
type,
normalize,
stride,
offset,
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(programInfo.attribLocations.vertexColor);
}
完整代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>WebGL Demo</title>
<script
src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.***/ajax/libs/gl-matrix/2.8.1/gl-matrix-min.js"
integrity="sha512-zhHQR0/H5SEBL3Wn6yYSaTTZej12z0hVZKOv3TwCUXT1z5qeqGcXJLLrbERYRScEDDpYIJhPC1fk31gqR783iQ=="
crossorigin="anonymous"
defer
></script>
<script src="webgl-demo.js" type="module"></script>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="glcanvas" width="640" height="480"></canvas>
</body>
</html>
// webgl-demo.js
import { initBuffers } from "./init-buffers.js";
import { drawScene } from "./draw-scene.js";
main();
function main() {
const canvas = document.querySelector("#glcanvas");
// Initialize the GL context
const gl = canvas.getContext("webgl");
// Only continue if WebGL is available and working
if (gl === null) {
alert(
"Unable to initialize WebGL. Your browser or machine may not support it."
);
return;
}
// Set clear color to black, fully opaque
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
// Clear the color buffer with specified clear color
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Vertex shader program
const vsSource = `
attribute vec4 aVertexPosition;
attribute vec4 aVertexColor;
uniform mat4 uModelViewMatrix;
uniform mat4 uProjectionMatrix;
varying lowp vec4 vColor;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = uProjectionMatrix * uModelViewMatrix * aVertexPosition;
vColor = aVertexColor;
}
`;
// Fragment shader program
const fsSource = `
varying lowp vec4 vColor;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vColor;
}
`;
// Initialize a shader program; this is where all the lighting
// for the vertices and so forth is established.
const shaderProgram = initShaderProgram(gl, vsSource, fsSource);
// 收集shader program.
// 查找使用到了哪些shader program
// 获取aVertexColor和aVertexPosition变量
// 查找uniform locations.
const programInfo = {
program: shaderProgram,
attribLocations: {
vertexPosition: gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, "aVertexPosition"),
vertexColor: gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, "aVertexColor"),
},
uniformLocations: {
projectionMatrix: gl.getUniformLocation(
shaderProgram,
"uProjectionMatrix"
),
modelViewMatrix: gl.getUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "uModelViewMatrix"),
},
};
// Here's where we call the routine that builds all the
// objects we'll be drawing.
const buffers = initBuffers(gl);
// Draw the scene
drawScene(gl, programInfo, buffers);
}
// 初始化顶点着色器和片着色器
function initShaderProgram(gl, vsSource, fsSource) {
const vertexShader = loadShader(gl, gl.VERTEX_SHADER, vsSource);
const fragmentShader = loadShader(gl, gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, fsSource);
// Create the shader program
const shaderProgram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram);
// If creating the shader program failed, alert
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(shaderProgram, gl.LINK_STATUS)) {
alert(
`Unable to initialize the shader program: ${gl.getProgramInfoLog(
shaderProgram
)}`
);
return null;
}
return shaderProgram;
}
// 加载和编译着色器
function loadShader(gl, type, source) {
const shader = gl.createShader(type);
// Send the source to the shader object
gl.shaderSource(shader, source);
// ***pile the shader program
gl.***pileShader(shader);
// See if it ***piled su***essfully
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.***PILE_STATUS)) {
alert(
`An error o***urred ***piling the shaders: ${gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader)}`
);
gl.deleteShader(shader);
return null;
}
return shader;
}
// init-buffers.js
function initBuffers(gl) {
const positionBuffer = initPositionBuffer(gl);
const colorBuffer = initColorBuffer(gl);
return {
position: positionBuffer,
color: colorBuffer,
};
}
// 设置顶点缓存
function initPositionBuffer(gl) {
// Create a buffer for the square's positions.
const positionBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
// Select the positionBuffer as the one to apply buffer
// operations to from here out.
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);
// Now create an array of positions for the square.
const positions = [1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0];
// Now pass the list of positions into WebGL to build the
// shape. We do this by creating a Float32Array from the
// JavaScript array, then use it to fill the current buffer.
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(positions), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
return positionBuffer;
}
// 将顶点颜色写入缓冲区
function initColorBuffer(gl) {
const colors = [
1.0,
1.0,
1.0,
1.0, // white
1.0,
0.0,
0.0,
1.0, // red
0.0,
1.0,
0.0,
1.0, // green
0.0,
0.0,
1.0,
1.0, // blue
];
const colorBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(colors), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
return colorBuffer;
}
export { initBuffers };
// draw-scene.js
function drawScene(gl, programInfo, buffers) {
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // Clear to black, fully opaque
gl.clearDepth(1.0); // Clear everything
gl.enable(gl.DEPTH_TEST); // Enable depth testing
gl.depthFunc(gl.LEQUAL); // Near things obscure far things
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | gl.DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
const fieldOfView = (45 * Math.PI) / 180; // in radians
const aspect = gl.canvas.clientWidth / gl.canvas.clientHeight;
const zNear = 0.1;
const zFar = 100.0;
const projectionMatrix = mat4.create();
// 创建一个透视投影矩阵,该矩阵定义了观察者视角下的透视效果,用于将 3D 场景投影到 2D 屏幕上,实现透视效果
mat4.perspective(projectionMatrix, fieldOfView, aspect, zNear, zFar);
// Set the drawing position to the "identity" point, which is
// the center of the scene.
const modelViewMatrix = mat4.create();
// 将模型视图矩阵modelViewMatrix 沿着世界坐标系的z轴负方向移动6个单位
mat4.translate(
modelViewMatrix, // 表示结果存储的目标矩阵,即进行平移操作后的矩阵将存储在这里。
modelViewMatrix, // 表示要进行平移操作的原始矩阵,即待平移的矩阵。
[-0.0, 0.0, -6.0] // 表示一个包含 x、y 和 z 坐标的数组,指定了平移的距离和方向
);
// Tell WebGL how to pull out the positions from the position
// buffer into the vertexPosition attribute.
setPositionAttribute(gl, buffers, programInfo);
setColorAttribute(gl, buffers, programInfo);
// 绘制调用将使用该着色器程序中定义的顶点着色器和片元着色器来处理顶点和片元数据
gl.useProgram(programInfo.program);
// 设置shader中 uniforms值
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(
programInfo.uniformLocations.projectionMatrix,
false,
projectionMatrix
);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(
programInfo.uniformLocations.modelViewMatrix,
false,
modelViewMatrix
);
{
const offset = 0;
// 绘制的顶点数量,即条带中顶点的个数
const vertexCount = 4;
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLE_STRIP, offset, vertexCount);
}
}
// positionBuffer中读取值并赋值给vertexPosition属性.
function setPositionAttribute(gl, buffers, programInfo) {
const num***ponents = 2; // pull out 2 values per iteration
const type = gl.FLOAT; // the data in the buffer is 32bit floats
const normalize = false; // don't normalize
const stride = 0; // how many bytes to get from one set of values to the next
// 0 = use type and num***ponents above
const offset = 0; // how many bytes inside the buffer to start from
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffers.position);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
programInfo.attribLocations.vertexPosition,
num***ponents,
type,
normalize,
stride,
offset
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(programInfo.attribLocations.vertexPosition);
}
// 从colorBuffer中读取颜色属性并传递给vertexColor属性并指定步长
function setColorAttribute(gl, buffers, programInfo) {
// 当 num***ponents 被设置为 4 时,表示每个顶点的颜色数据由四个分量组成,分别对应 RGBA 中的红、绿、蓝和透明度。这样的设置可以确保在顶点着色器中正确地解析和处理颜色数据,以便在渲染过程中正确显示顶点的颜色
const num***ponents = 4;
const type = gl.FLOAT;
const normalize = false;
const stride = 0;
const offset = 0;
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffers.color);
// 指定如何从缓冲区中读取数据并将其传递给颜色属性
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
programInfo.attribLocations.vertexColor,
num***ponents,
type,
normalize,
stride,
offset
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(programInfo.attribLocations.vertexColor);
}
export { drawScene };
gl.uniformMatrix4fv 函数
将矩阵数据传递给顶点着色器中的 uniform 变量。这个函数用于传递 4x4 的矩阵数据给着色器程序。
下面是这两个函数调用的详细解释:
-
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(programInfo.uniformLocations.projectionMatrix, false, projectionMatrix);-
programInfo.uniformLocations.projectionMatrix是一个 uniform 变量的位置,它指定了顶点着色器中投影矩阵的 uniform 变量的位置。 -
false表示是否需要转置矩阵。在 WebGL 中,通常使用列主序(column-major)的矩阵表示,因此这里设置为false。 -
projectionMatrix是一个 4x4 投影矩阵,它包含了将顶点从世界坐标系变换到裁剪空间的变换信息。通过这个函数调用,将投影矩阵数据传递给顶点着色器中的projectionMatrixuniform 变量。
-
-
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(programInfo.uniformLocations.modelViewMatrix, false, modelViewMatrix);-
programInfo.uniformLocations.modelViewMatrix是另一个 uniform 变量的位置,它指定了顶点着色器中模型视图矩阵的 uniform 变量的位置。 -
false同样表示不需要转置矩阵。 -
modelViewMatrix是一个 4x4 模型视图矩阵,它包含了将顶点从模型空间变换到观察者空间的变换信息。通过这个函数调用,将模型视图矩阵数据传递给顶点着色器中的modelViewMatrixuniform 变量。
-
这样,通过 gl.uniformMatrix4fv 函数,可以将投影矩阵和模型视图矩阵等矩阵数据传递给顶点着色器中的相应 uniform 变量,以便在渲染过程中正确地对顶点进行变换和投影操作。
在 WebGL 中,顶点数据是通过顶点缓冲区对象传递给顶点着色器的。当设置顶点属性时,需要指定顶点属性变量从缓冲区中获取数据的方式。这包括数据的组件数量、数据类型、是否归一化、步长(stride)和偏移量(offset)等信息。
gl.vertexAttribPointer 函数
用于指定顶点属性变量如何从缓冲区中读取数据。下面是一些参数的含义:
-
index:指定要修改的顶点属性的索引。 -
size:指定每个顶点属性的分量数量,比如 2 表示二维向量,3 表示三维向量,4 表示四维向量。 -
type:指定数据的类型,比如gl.FLOAT表示 32 位浮点数。 -
normalized:指定是否应该将非浮点数型的数据归一化到特定范围。 -
stride:指定相邻两个顶点属性开始之间的偏移量,以字节为单位。 -
offset:指定顶点属性在缓冲区中的起始偏移量,以字节为单位。
通过这些参数的设置,顶点着色器就能够正确地从缓冲区中读取顶点数据,并将其应用于渲染过程中。在绘制过程中,WebGL 会按照顶点的顺序从缓冲区中读取数据,并将其传递给顶点着色器,确保每个顶点都对应着正确的顶点数据。
gl.drawArrays函数
用于根据顶点数组绘制图形。下面是这个函数调用的详细解释:
-
gl.drawArrays(mode, first, count)-
mode参数指定了绘制的图元类型,比如gl.TRIANGLES表示绘制三角形,gl.POINTS表示绘制点,gl.LINES表示绘制线段等。 -
offset参数指定了从顶点数组中的哪个位置开始绘制,即起始索引。 -
vertexCount参数指定了要绘制的顶点数量。
-
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLE_STRIP, offset, vertexCount) 的含义是以三角形条带(triangle strip)的方式绘制图形。具体解释如下:
-
gl.TRIANGLE_STRIP表示使用三角形条带的方式绘制图形。在三角形条带中,每个顶点都会与前两个顶点组成一个三角形,因此顶点的顺序非常重要。 -
offset参数指定从顶点数组中的哪个位置开始绘制,即起始顶点的索引。 -
vertexCount参数指定了要绘制的顶点数量,即条带中顶点的个数。
通过这个函数调用,WebGL 将根据指定的顶点数组数据以三角形条带的方式绘制图形,根据顶点的顺序依次连接顶点来形成三角形条带。

