开始就进入微服务阶段
javase:OOP
MySQL:持久化
html+css+js+jquery+框架:视图,框架不熟练,css不好
javaweb:独立开发MVC三层架构的网站:原始
ssm:框架:简化了我们的开发流程,配置也开始较为复杂;
之前项目打包都是war包,程序在Tomcat中运行
spring再简化:springBoot-jar包,内嵌Tomcat;微服务架构!
服务越来越多:springCloud
1、SpringBoot简介
1.1、回顾什么是Spring
什么是Spring
Spring是一个开源框架,2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,作者:Rod Johnson 。
Spring是为了解决企业级应用开发的复杂性而创建的,简化开发。
Spring是如何简化Java开发的
为了降低Java开发的复杂性,Spring采用了以下4种关键策略:
-
基于POJO的轻量级和最小侵入性编程,所有东西都是bean;
-
通过IOC,依赖注入(DI)和面向接口实现松耦合;
-
基于切面(AOP)和惯例进行声明式编程;
-
通过切面和模版减少样式代码,RedisTemplate,xxxTemplate;
1.2、什么是SpringBoot
学过javaweb的同学就知道,开发一个web应用,从最初开始接触Servlet结合Tomcat, 跑出一个Hello Wolrld程序,是要经历特别多的步骤;后来就用了框架Struts,再后来是SpringMVC,到了现在的SpringBoot,过一两年又会有其他web框架出现;你们有经历过框架不断的演进,然后自己开发项目所有的技术也在不断的变化、改造吗?建议都可以去经历一遍;
所有的技术框架的发展似乎都遵循了一条主线规律:从一个复杂应用场景 衍生 一种规范框架,人们只需要进行各种配置而不需要自己去实现它,这时候强大的配置功能成了优点;发展到一定程度之后,人们根据实际生产应用情况,选取其中实用功能和设计精华,重构出一些轻量级的框架;之后为了提高开发效率,嫌弃原先的各类配置过于麻烦,于是开始提倡“约定大于配置”,进而衍生出一些一站式的解决方案。
是的这就是Java企业级应用->J2EE->spring->springboot的过程。
随着 Spring 不断的发展,涉及的领域越来越多,项目整合开发需要配合各种各样的文件,慢慢变得不那么易用简单,违背了最初的理念,甚至人称配置地狱。spring boot 正是在这样的一个背景下被抽象出来的开发框架,目的为了让大家更容易的使用 Spring 、更容易的集成各种常用的中间件、开源软件;
Spring Boot 基于 Spring 开发,Spirng Boot 本身并不提供 Spring 框架的核心特性以及扩展功能,只是用于快速、敏捷地开发新一代基于 Spring 框架的应用程序。也就是说,它并不是用来替代 Spring 的解决方案,而是和 Spring 框架紧密结合用于提升 Spring 开发者体验的工具。Spring Boot 以约定大于配置的核心思想,默认帮我们进行了很多设置,多数 Spring Boot 应用只需要很少的 Spring 配置。同时它集成了大量常用的第三方库配置(例如 Redis、MongoDB、Jpa、RabbitMQ、Quartz 等等),Spring Boot 应用中这些第三方库几乎可以零配置的开箱即用。
简单来说就是SpringBoot其实不是什么新的框架,它默认配置了很多框架的使用方式,就像maven整合了所有的jar包,spring boot整合了所有的框架 。
Spring Boot 出生名门,从一开始就站在一个比较高的起点,又经过这几年的发展,生态足够完善,Spring Boot 已经当之无愧成为 Java 领域最热门的技术。
Spring Boot的主要优点:
- 为所有Spring开发者更快的入门
- 开箱即用,提供各种默认配置来简化项目配置
- 内嵌式容器简化Web项目
- 没有冗余代码生成和XML配置的要求
1.3、微服务架构
微服务是一种架构风格,他要求我们在开发一个应用的时候,这个应用必须建成一系列小服务组合,可以通过http方式进行通信。
所谓微服务加购,就是打破之前all in one的架构方式,把每个功能元素独立出来,把独立出来的功能元素的动态组合,需要的功能元素才去拿来组合,需要多一些可以整合多个功能元素,所以微服务架构是对功能元素进行赋值,而没有对整个应用进行复制,这样做的好处是:
- 节省了调用资源
- 每个功能元素的服务都是一个可替换的,可独立升级的软件代码
程序核心:高内聚(在划分模块时,要把功能关系紧密的放到一个模块中)
低耦合(模块之间的联系越少越好,接口越简单越好)
论文地址:https://blog.csdn.***/qq_34831748/article/details/117318860
构建微服务分工:
- 构建一个个功能独立的微服务应用单元,可以使用springboot,可以帮我们快速构建一个应用
- 大型分布式网络服务的调用,这部分springcloud来完成,实现分布式
- 在分布式中间,进行流式数据计算,批处理,我们有spring cloud data flow
- spring为我们想清楚了整个开始构建应用到大型分布式应用全流程方案
2、第一个SpringBoot程序
2.1环境配置
环境准备:
- java version “1.8.0_181”
- Maven-3.6.1
- SpringBoot 2.x 最新版
开发工具:
- IDEA
2.2创建基础项目说明
Spring官方提供了非常方便的工具让我们快速构建应用,IDEA也集成了这个网站
Spring Initializr:https://start.spring.io/
2.2.1项目创建方式一
使用Spring Initializr 的 Web页面创建项目
-
打开 https://start.spring.io/
-
填写项目信息
-
点击”Generate Project“按钮生成项目;下载此项目
-
解压项目包,并用IDEA以Maven项目导入,一路下一步即可,直到项目导入完毕。
-
如果是第一次使用,可能速度会比较慢,包比较多、需要耐心等待一切就绪。
2.2.2项目创建方式二
-
使用 IDEA 直接创建项目
-
创建一个新项目
-
选择spring initalizr , 可以看到默认就是去官网的快速构建工具那里实现
-
填写项目信息
-
选择初始化的组件(初学勾选 Web 即可)
-
填写项目路径
-
等待项目构建成功
2.2.3项目结构分析:
- 程序的主启动类(程序的主入口)HelloController
- 一个 application.properties 配置文件(SpringBoot的核心配置文件)
- 一个 测试类 HelloWorldApplicationTests
- 一个 pom.xml
pom.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>***.hwt</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>HelloWorld</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- web依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<!--spring-boot-starter-web是所有springboot依赖的前缀-->
</dependency>
<!--单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!--打jar包插件-->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
编写一个http接口
-
在主程序的同级目录下,新建一个controller包,一定要在同级目录下,否则识别不到
-
在包中新建一个HelloController类
//自动装配 @RestController public class HelloController { //接口:http://localhost:8080/hello @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ //调用业务 return "hello,world"; } } -
测试运行通过访问localhost:8080/hello浏览器输出hello,world
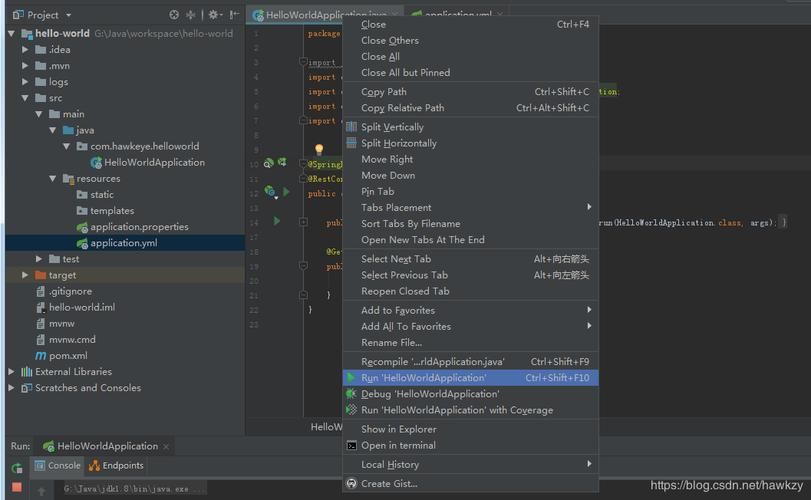
2.2.4、项目打jar包
-
点击maven里的package
-
在target会得到一个jar包
-
执行命令:java -jar .\demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
-
测试在浏览器访问(http://localhost:8080/hello)
彩蛋
更改启动时显示的字符拼成的字母,修改banne图案
到项目下的 resources 目录下新建一个banner.txt 即可。
图案:https://www.bootschool.***/ascii 这个网站生成,然后拷贝到文件中即可!
2.3运行原理初探
2.3.1pom.xml
父依赖
核心依赖在父工程中
这里我们在引入一些SpringBoot依赖的时候,不需要指定版本,就因为有这些版本仓库
其中它主要是依赖一个父项目,主要是管理项目的资源过滤及插件!
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.9</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
点进去会发现还有一个父依赖:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.7.9</version>
</parent>
这里才是真正管理SpringBoot应用里面所有依赖版本的地方,SpringBoot的版本控制中心;
以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;但是如果导入的包没有在依赖中管理着就需要手动配置版本了;
启动器 spring-boot-starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 启动器:就是SpringBoot的启动场景
- 比如spring-boot-starter-web,会帮我们自动导入web环境所有的依赖
- springboot会将所有功能场景,都变成一个个的启动器
- 我们要是用什么功能,就需要找到一个个启动器就可以了
主启动类
//标注这是一个springBoot启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot01HelloworldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//通过这个方法将springboot启动
SpringApplication.run(Springboot01HelloworldApplication.class, args);
}
}
-
@SpringBootApplication:springBoot配置
@SpringBootConfiguration //spring配置类 @***ponentScan //说明这也是一个spring的组件-
@EnableAutoConfiguration : 自动配置
@AutoConfigurationPackage //自动配置包 @Import({Registrar.class}) //导入了选择器 @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})//自动配置选择容器 protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes)//获取所有配置 -
获取候选的配置
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List<String> configurations = new ArrayList(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader())); ImportCandidates.load(AutoConfiguration.class, this.getBeanClassLoader()).forEach(configurations::add); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories nor in META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }
-
-
META-INF/spring.factories:自动配置的核心文件
结构图:
SpringBoot所有的自动配置,都在启动类中被扫描并加载:所有的自动配置类都在这里面,但是不一定生效,要判断条件是否成立,只要导入了对应的starter们就有对应的启动器了,有了启动器,我们的自动装配就会生效,然后就配置成功了
- SpringBoot在启动的时候,从类路径下/META-INF/spring.factories获取指定的值
- 将这些自动配置的类导入容器,自动配置类就会生效,帮我们进行自动配置
- 以前我们需要自动配置的东西,现在不需要了
- 整合javaEE,解决方案和自动配置的东西都在Spring-boot-autoconfigure下
- 它会把所有需要导入的组件,以类名的方式返回这些组件,这些组件就会被添加到容器
- 容器中也会存在非常多的XXXAutoConfigure的文件(@Bean),就是这个类给容器导入了这个场景所需要的所有组件并自动配置
SpringApplication
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
SpringApplication.run分析
分析该方法主要分两部分,一部分是SpringApplication的实例化,二是run方法的执行;
SpringApplication这个类主要做了以下四件事情:
1、推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是Web项目
2、查找并加载所有可用初始化器 , 设置到initializers属性中
3、找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners属性中
4、推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类
run方法流程分析:
关于SpringBoot,谈谈你的理解:
- 自动装配:如何加载
- run方法:如何启动
全面接管SpringMVC的配置!
3、yaml语法
3.1 yaml概述
配置文件:
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件 , 配置文件名称是固定的
-
application.properties
- 语法结构 :key=value
-
application.yml
- 语法结构 :key:空格 value
**配置文件的作用 :**修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值,因为SpringBoot在底层都给我们自动配置好了;
比如我们可以在配置文件中修改Tomcat 默认启动的端口号!测试一下!
YAML是 “YAML Ain’t a Markup Language” (YAML不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:“Yet Another Markup Language”(仍是一种标记语言)
这种语言以数据作为中心,而不是以标记语言为重点!
以前的配置文件,大多数都是使用xml来配置;比如一个简单的端口配置,我们来对比下yaml和xml
传统xml配置:
<server>
<port>8081<port>
</server>
yaml配置:
server:
prot: 8081
yaml基础语法:
# k-v键值对
# 对空格要求十分高
name: gaoqiqiang
#相当于name=xiaoqi
# 存对象
student:
name: gaoqiqiang
age: 40
# 行内写法
student1: {name: gaoqiqiang,age: 40}
# 对象使用{ } 数组使用 [ ]
#数组
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
pets1: [cat,dog,pig]
语法要求十分严格!
1、空格不能省略
2、以缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左边对齐的一列数据都是同一个层级的。
3、属性和值的大小写都是十分敏感的。
3.2、yaml语法测试
-
Person类
@***ponent public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; private boolean happy; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> map; private List<Object> list; private Dog dog; }@***ponent public class Dog { @Value(("旺财")) private String name; @Value("5") private Integer age; } -
application.yaml
person: name: 高启强 age: 5 happy: false birth: 2023/03/08 map: {k1: v1,k2: v2} list: - code - music dog: name: 旺财 age: 3springboot配置注解处理器没有找到
@***ponent @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; private boolean happy; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> map; private List<Object> list; private Dog dog; }导入文件:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> -
测试类中进行测试
@SpringBootTest class Springboot02ConfigApplicationTests { //@Autowired //private Dog dog; @Autowired private Person person; @Test void contextLoads() { // System.out.println(dog); System.out.println(person); } } -
通过测试或得到了所有yaml数据
3.3、加载指定配置文件
-
新建一个application.properties文件
name=高启强 -
修改之前的Person类
//指定配置文件 @PropertySource(value = "classpath:application1.properties") public class Person { //spel表达式取出配置文件的值 @Value("${name}") private String name; private Integer age; private boolean happy; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> map; private List<Object> list; private Dog dog; } -
测试后得到name=高启强
配置文件占位符
person:
name: 高启强${random.uuid} # 生成随机uuid
age: ${random.int} #随机数
happy: false
birth: 2023/03/08
map: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
list:
- code
- music
dog:
name: ${person.hello:hello}_旺财 # 占位符
age: 3
对比小结:
@Value这个使用起来并不友好!我们需要为每个属性单独注解赋值,比较麻烦;我们来看个功能对比图
-
@ConfigurationProperties只需要写一次即可 , @Value则需要每个字段都添加
-
**松散绑定:**这个什么意思呢? 比如我的yaml中写的last-name,这个和lastName是一样的, - 后面跟着的字母默认是大写的。这就是松散绑定。可以测试一下
-
JSR303数据校验 , 这个就是我们可以在字段是增加一层过滤器验证 , 可以保证数据的合法性
-
复杂类型封装,yaml中可以封装对象 , 使用value就不支持。
结论
配置yaml和配置properties都可以获取到值 , 但是强烈推荐 yaml;
如果我们在某个业务中,只需要获取配置文件中的某个值,可以使用一下 @value;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个JavaBean来和配置文件进行一一映射,就直接@configurationProperties,不要犹豫!
4、 JSR303数据校验及多环境切换
4.1、 JSR303数据校验
使用:
Springboot中可以用@validated来校验数据,如果数据异常则会统一抛出异常,方便异常中心统一处理。我们这里来写个注解让我们的name只能支持Email格式;
@***ponent
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated //数据校验
public class Person {
@Email(message="邮箱格式错误") //name必须是邮箱格式
private String name;
运行结果:
Property: person.name
Value: 高启强1390d6b9-6380-4b42-ada6-d1567633fe6d
Origin: class path resource [application.yaml] - 2:9
Reason: 邮箱格式错误
常见参数:
@NotNull(message="名字不能为空")
private String userName;
@Max(value=120,message="年龄最大不能查过120")
private int age;
@Email(message="邮箱格式错误")
private String email;
空检查
@Null 验证对象是否为null
@NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格.
@NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.
Booelan检查
@AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
@AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
长度检查
@Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Length(min=, max=) string is between min and max included.
日期检查
@Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
@Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
@Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
数值检查
建议使用在Stirng,Integer类型,不建议使用在int类型上,因为表单值为“”时无法转换为int,但可以转换为Stirng为”“,Integer为null
@Min 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否大等于指定的值
@Max 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否小等于指定的值
@DecimalMax 被标注的值必须不大于约束中指定的最大值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最大值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
@DecimalMin 被标注的值必须不小于约束中指定的最小值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最小值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
@Digits 验证 Number 和 String 的构成是否合法
@Digits(integer=,fraction=) 验证字符串是否是符合指定格式的数字,interger指定整数精度,fraction指定小数精度。
@Range(min=, max=) 被指定的元素必须在合适的范围内
@Range(min=10000,max=50000,message=”range.bean.wage”)
@Valid 递归的对关联对象进行校验, 如果关联对象是个集合或者数组,那么对其中的元素进行递归校验,如果是一个map,则对其中的值部分进行校验.(是否进行递归验证)
@CreditCardNumber信用卡验证
@Email 验证是否是邮件地址,如果为null,不进行验证,算通过验证。
@ScriptAssert(lang= ,script=, alias=)
@URL(protocol=,host=, port=,regexp=, flags=)]()]()
4.2 、多环境切换
profile是Spring对不同环境提供不同配置功能的支持,可以通过激活不同的环境版本,实现快速切换环境;
多配置文件:
我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml , 用来指定多个环境版本;
例如:
-
application-test.properties 代表测试环境配置
-
application-dev.properties 代表开发环境配置
但是Springboot并不会直接启动这些配置文件,它默认使用application.properties主配置文件;
我们需要通过一个配置来选择需要激活的环境:
#比如在配置文件中指定使用dev环境,我们可以通过设置不同的端口号进行测试;
#我们启动SpringBoot,就可以看到已经切换到dev下的配置了;
spring.profiles.active=dev
外部加载配置文件的方式和优先级:
-
优先级1:项目路径下的config文件夹配置文件
-
优先级2:项目路径下配置文件
-
优先级3:资源路径下的config文件夹配置文件
-
优先级4:资源路径下配置文件
优先级由高到底,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置;
#配置项目的访问路径
server.servlet.context-path=/kuang
多文档块:
和properties配置文件中一样,但是使用yml去实现不需要创建多个配置文件,更加方便了
yaml通过三个-来分割模块
#选择要激活那个环境块
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
server:
port: 8081
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev #配置环境的名称
---
server:
port: 8084
spring:
profiles: prod #配置环境的名称
拓展:
指定位置加载配置文件
我们还可以通过spring.config.location来改变默认的配置文件位置
项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置;这种情况,一般是后期运维做的多,相同配置,外部指定的配置文件优先级最高
java -jar spring-boot-config.jar --spring.config.location=F:/application.properties
5、自动装配原理
5.1、 自动装配原理详解
我们以**HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)**为例解释自动配置原理;
//表示这是一个配置类,和以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件;
@Configuration
//启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;
//进入这个HttpProperties查看,将配置文件中对应的值和HttpProperties绑定起来;
//并把HttpProperties加入到ioc容器中
@EnableConfigurationProperties({HttpProperties.class})
//Spring底层@Conditional注解
//根据不同的条件判断,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效;
//这里的意思就是判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(
type = Type.SERVLET
)
//判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器;
@ConditionalOnClass({CharacterEncodingFilter.class})
//判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置:spring.http.encoding.enabled;
//如果不存在,判断也是成立的
//即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的;
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "spring.http.encoding",
value = {"enabled"},
matchIfMissing = true
)
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
//他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了
private final Encoding properties;
//只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties.getEncoding();
}
//给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean //判断容器没有这个组件?
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.REQUEST));
filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.RESPONSE));
return filter;
}
}
根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效!
- 一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;
- 这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
- 所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装着;
- 配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
原先需要在bean中手打的属性(property)封装成了一个类,然后通过yaml文件进行自动注入,而我们也可以在application.yaml文件中对这些property进行赋值。
//从配置文件中获取指定的值和bean的属性进行绑定
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http")
public class HttpProperties {
// .....
}
精髓:
- SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
- 我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中;
- 我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
- 给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可;
**xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;**给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性;
6、SpringBoot Web开发
之前的项目都是jar包结尾的,没有存放webapp的地方!!!!!!
SpringBoot最大的特点就是自动装配
创建应用,选择模块导入starter,只需要专注于业务代码
springboot到底帮我们配置了什么,我们能不能修改?能修改哪些东西?能不能扩展
-
xxxAutoConfiguration:向容器中自动配置组件
-
xxxProperties:自动配置类,装配配置文件中自定义的一些内容
要解决的问题:
-
导入静态资源html,css,js
-
首页
-
写jsp的地方,模板引擎Thymeleaf
-
装配和扩展SpringMVC
-
增删改查
-
拦截器
-
国际化
6.1、静态资源处理
addResourceHandlers 添加资源处理
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
// 已禁用默认资源处理
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
// 缓存控制
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
// webjars 配置
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/")
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
// 静态资源配置
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern)
.addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
6.1.1、webjars
Webjars本质就是以jar包的方式引入我们的静态资源 , 我们以前要导入一个静态资源文件,直接导入即可。
使用SpringBoot需要使用Webjars,我们可以去搜索一下:
网站:https://www.webjars.org
要使用jQuery,我们只要要引入jQuery对应版本的pom依赖即可!
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>
导入完毕,查看webjars目录结构,并访问Jquery.js文件!
只要是静态资源,SpringBoot就会去对应的路径寻找资源:通过访问网站http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.js
很少使用webjars!!!
6.1.2、静态资源映射规律
- 在springboot,我们可以使用一下方式处理静态数据
- webjars
localhost:8080/webjars/ - public,static,/**,resources
localhost:8080/
- webjars
- 优先级:resources>static(默认)>public
测试:
-
分别在几个目录下创建名为1.js的文件
-
访问:http://localhost:8080/1.js
6.1.3、自定义资源路径
也可以自己通过配置文件来指定一下,哪些文件夹是需要我们放静态资源文件的,在application.properties中配置;
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/coding/,classpath:/koko/
6.1.4、首页处理
Spring Boot在配置的静态内容位置中查找 favicon.ico。如果存在这样的文件,它将自动用作应用程序的favicon。
关闭默认图标
#关闭默认图标
spring.mvc.favicon.enabled=false
6.2 Thymeleaf
6.2.1、模板引擎介绍
前端交给我们的页面,是html页面。如果是我们以前开发,我们需要把他们转成jsp页面,jsp好处就是当我们查出一些数据转发到JSP页面以后,我们可以用jsp轻松实现数据的显示,及交互等。
jsp支持非常强大的功能,包括能写Java代码,但是呢,我们现在的这种情况,SpringBoot这个项目首先是以jar的方式,不是war,像第二,我们用的还是嵌入式的Tomcat,所以呢,他现在默认是不支持jsp的。
那不支持jsp,如果我们直接用纯静态页面的方式,那给我们开发会带来非常大的麻烦,那怎么办呢?
- SpringBoot推荐你可以来使用模板引擎:
模板引擎,我们其实大家听到很多,其实jsp就是一个模板引擎,还有用的比较多的freemarker,包括SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf,模板引擎有非常多,但再多的模板引擎,他们的思想都是一样的,什么样一个思想呢我们来看一下这张图:
模板引擎的作用就是我们来写一个页面模板,比如有些值呢,是动态的,我们写一些表达式。而这些值,从哪来呢,就是我们在后台封装一些数据。然后把这个模板和这个数据交给我们模板引擎,模板引擎按照我们这个数据帮你把这表达式解析、填充到我们指定的位置,然后把这个数据最终生成一个我们想要的内容给我们写出去,这就是我们这个模板引擎,不管是jsp还是其他模板引擎,都是这个思想。只不过呢,就是说不同模板引擎之间,他们可能这个语法有点不一样。其他的我就不介绍了,我主要来介绍一下SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf模板引擎,这模板引擎呢,是一个高级语言的模板引擎,他的这个语法更简单。而且呢,功能更强大。
6.2.2、引入Thymeleaf
怎么引入呢,对于springboot来说,什么事情不都是一个start的事情嘛,我们去在项目中引入一下。给大家三个网址:
Thymeleaf 官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/
Thymeleaf 在Github 的主页:https://github.***/thymeleaf/thymeleaf
Spring官方文档:找到我们对应的版本
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.2.5.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#using-boot-starter
pom依赖:
<dependency>
<!--都是基于3.xx开发的-->
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId>
</dependency>
结论:使用Thymeleaf,只需要导入对应的依赖即可,如果想要访问页面,我们将html放入Templates目录下即可
测试:
-
在下创建测试用的test网页
-
导入thymeleaf-spring5jar包
-
创建controller类
//在templates目录下的所有页面,只能通过controller来跳转 //这个需要模板引擎的支持! Thymeleaf @RestController public class HelloController { @GetMapping("/test") public String hello(){ return "test"; } } -
浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/test
6.2.3、Thymeleaf语法学习
Thymeleaf 官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/
测试:
-
修改测试请求,增加数据传输;
//在templates目录下的所有页面,只能通过controller来跳转 //这个需要模板引擎的支持! Thymeleaf @Controller public class HelloController { @GetMapping("/t1") public String hello(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","hello,Thymeleaf"); return "test"; } } -
使用thymeleaf,需要在html文件中导入命名空间的约束,方便提示。
-
我们去编写下前端页面
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>测试</title> </head> <body> <h1>测试页面</h1> <!--th:text就是将div中的内容设置为它指定的值,和之前学习的Vue一样--> <div th:text="${msg}"></div> </body> </html> -
访问:(http://localhost:8080/test)
如果没有访问到页面原因在于测试请求中用的是@RestController注解,修改为@Controller即可
- 简单表达式:
- 变量表达式:
${...} - 选择变量表达式:
*{...} - 消息表达式:
#{...} - 链接网址表达式:
@{...} - 片段表达式:
~{...}
- 变量表达式:
- 文字
- 文本文本:,,…
'one text'``'Another one!' - 数字文字: , , , ,…
0``34``3.0``12.3 - 布尔文字: ,
true``false - 空文本:
null - 文字标记: , , ,…
one``sometext``main
- 文本文本:,,…
- 文本操作:
- 字符串串联:
+ - 文字替换:
|The name is ${name}|
- 字符串串联:
- 算术运算:
- 二元运算符: , , , , ,
+``-``*``/``% - 减号(一元运算符):
-
- 二元运算符: , , , , ,
- 布尔运算:
- 二元运算符: ,
and``or - 布尔否定(一元运算符):,
!``not
- 二元运算符: ,
- 比较和平等:
- 比较器: , , , ( , , ,
>``<``>=``<=``gt``lt``ge``le) - 等运算符: , (,
==``!=``eq``ne)
- 比较器: , , , ( , , ,
- 条件运算符:
- 如果-那么:
(if) ? (then) - 如果-然后-否则:
(if) ? (then) : (else) - 违约:
(value) ?: (defaultvalue)
- 如果-那么:
- 特殊代币:
- 无操作:
_
- 无操作:
测试:
-
text.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>测试</title> </head> <body> <h1>测试页面</h1> <!--th:text就是将div中的内容设置为它指定的值,和之前学习的Vue一样--> <div th:text="${msg}"></div> <div th:utext="${msg}"></div> <hr> <h3 th:each="user:${users}" th:text="${user}"></h3> </body> </html> -
控制器
@Controller public class HelloController { @GetMapping("/test") public String hello(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","<h1>hello,Thymeleaf</h1>"); model.addAttribute("users", Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb")); return "test"; } } -
测试:http://localhost:8080/test
7、MVC配置原理
7.1、自动配置原理
在进行项目编写前,我们还需要知道一个东西,就是SpringBoot对我们的SpringMVC还做了哪些配置,包括如何扩展,如何定制。
途径一:源码分析,
途径二:官方文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.2.5.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-spring-mvc-auto-configuration
Spring MVC Auto-configuration
// Spring Boot为Spring MVC提供了自动配置,它可以很好地与大多数应用程序一起工作。
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.
// 自动配置在Spring默认设置的基础上添加了以下功能:
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
// 包含视图解析器
Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.
// 支持静态资源文件夹的路径,以及webjars
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars
// 自动注册了Converter:
// 转换器,这就是我们网页提交数据到后台自动封装成为对象的东西,比如把"1"字符串自动转换为int类型
// Formatter:【格式化器,比如页面给我们了一个2019-8-10,它会给我们自动格式化为Date对象】
Automatic registration of Converter, Generi***onverter, and Formatter beans.
// HttpMessageConverters
// SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的的,比如我们要把一个User对象转换为JSON字符串,可以去看官网文档解释;
Support for HttpMessageConverters (covered later in this document).
// 定义错误代码生成规则的
Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver (covered later in this document).
// 首页定制
Static index.html support.
// 图标定制
Custom Favicon support (covered later in this document).
// 初始化数据绑定器:帮我们把请求数据绑定到JavaBean中!
Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean (covered later in this document).
/*
如果您希望保留Spring Boot MVC功能,并且希望添加其他MVC配置(拦截器、格式化程序、视图控制器和其他功能),则可以添加自己
的@configuration类,类型为webmv***onfiguer,但不添加@EnableWebMvc。如果希望提供
RequestMappingHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerAdapter或ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的自定义
实例,则可以声明WebMVCregistrationAdapter实例来提供此类组件。
*/
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration
(interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own
@Configuration class of type WebMv***onfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide
custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such ***ponents.
// 如果您想完全控制Spring MVC,可以添加自己的@Configuration,并用@EnableWebMvc进行注释。
If you want to take ***plete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
我们来仔细对照,看一下它怎么实现的,它告诉我们SpringBoot已经帮我们自动配置好了SpringMVC,然后自动配置了哪些东西呢?
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 内容协商视图解析器
8、员工管理系统
静态资源链接:https://pan.baidu.***/s/1JJqRWQA3Jcdzk7BfhXhTqw
提取码:vysx
8.1、首页实现
在每个静态页面添加头文件
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
把所有的路径都修改为thymeleaf
<link th:href="@{asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css}" rel="stylesheet">
8.2、国际化
编写i18n国际化资源文件
其中新建三个配置文件,用来配置语言:
login.properties:无语言配置时候生效login_en_US.properties:英文生效login_zh_***.properties:中文生效
命名方式是下划线的组合:文件名_语言_国家.properties;
-
login.properties
login.tip=请登录
login.password=密码
login.remember=记住我
login.btn=登录
login.username=用户名 -
login_en_US.properties
login.tip=Please sign in
login.password=password
login.remember=remember me
login.btn=login
login.username=username -
login_zh_***.properties
login.tip=请登录
login.password=密码
login.remember=记住我
login.btn=登录
login.username=用户名
配置国际化资源文件名称
在Spring程序中,国际化主要是通过
ResourceBundleMessageSource这个类来实现的Spring Boot通过
MessageSourceAutoConfiguration为我们自动配置好了管理国际化资源文件的组件
-
实现LocaleResolver接口
public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver { //解析请求 @Override public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) { //获取请求中的国际化参数 String language = request.getParameter("l"); //默认的地区 Locale locale = Locale.getDefault(); //如果请求的链接参数不为空,携带了国际化参数 if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(language)) { String[] split = language.split("_");//zh_***(语言_地区) locale = new Locale(split[0], split[1]); } return locale; } @Override public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) { } } -
编写bean
@Configuration //@EnableWebMvc public class MyMv***onfig implements WebMv***onfigurer { //视图跳转 @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index"); registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("index"); registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard"); } @Bean public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){ return new MyLocaleResolver(); } } -
前端页面添加中英文切换标签
<!-- 这里传入参数不需要使用 ?使用 (key=value)--> <a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='zh_***')}">中文</a> <a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='en_US')}">English</a>
8.3、登录功能的实现
-
前端页面编写一个提交地址并且添加name属性为后端传参
<form class="form-signin" th:action="@{/user/login}"> <img class="mb-4" th:src="@{/asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg}" alt="" width="72" height="72"> <h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal" th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign in</h1> <!-- 如果msg的值为空则不显示消息--> <p style="color: red" th:text="${msg}" th:if="${not #strings.isEmpty(msg)}"></p> <input type="text" name="username" class="form-control" th:placeholder="#{login.username}" required="" autofocus=""> <input type="password" name="password" class="form-control" th:placeholder="#{login.password}" required=""> <div class="checkbox mb-3"> <label> <input type="checkbox" value="remember-me" > [[#{login.remember}]] </label> </div> <button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit" >[[#{login.btn}]]</button> <p class="mt-5 mb-3 text-muted">© 2017-2018</p> <!-- 这里传入参数不需要使用 ?使用 (key=value)--> <a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='zh_***')}">中文</a> <a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='en_US')}">English</a> </form> -
后端接收参数并且控制视图跳转
@Controller public class LoginController { @RequestMapping("/user/login") // @ResponseBody public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username , @RequestParam("password") String password, Model model){ if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(username)&&"123456".equals(password)){ return "redirect:/main.html"; }else { model.addAttribute("msg","用户名或者密码错误"); return "index"; } } }mvc控制器添加视图跳转
registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard"); -
前端接收msg参数并且展示
8.4、拦截器
为了解决上述遗留的问题,我们需要自定义一个拦截器;
在config目录下,新建一个登录拦截器类LoginHandlerInterceptor
用户登录成功后,后台会得到用户信息;如果没有登录,则不会有任何的用户信息;
我们就可以利用这一点通过拦截器进行拦截:
- 当用户登录时将用户信息存入session中,访问页面时首先判断session中有没有用户的信息
- 如果没有,拦截器进行拦截;
- 如果有,拦截器放行
-
首先需要将用户登录后的信息存入session
@Controller public class LoginController { @RequestMapping("/user/login") // @ResponseBody public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username , @RequestParam("password") String password, Model model, HttpSession session){ if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(username)&&"123456".equals(password)){ session.setAttribute("loginUser",username); return "redirect:/main.html"; }else { model.addAttribute("msg","用户名或者密码错误"); return "index"; } } } -
自定义一个拦截器实现LoginHandlerInterceptor接口
public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { //用户登录成功后,应该有自己的session Object session = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser"); if (session == null) { request.setAttribute("msg", "权限不够,请先登录"); request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request, response); return false; } else { return true; } } } -
然后配置到bean中注册,在
MyMv***onfig配置类中,重写关于拦截器的方法,添加我们自定义的拦截器,注意屏蔽静态资源及主页以及相关请求的拦截@Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor()) .addPathPatterns("/**") .excludePathPatterns("/index.html", "/", "/user/login", "/asserts/**"); } -
重启主程序进行测试,直接访问http://localhost:8080/main.html
8.5、查询员工信息
实现视图跳转:
-
给
dashboard.html页面中Customers部分标签添加href属性,实现点击该标签请求/emps路径跳转到list.html展示所有的员工信息<li class="nav-item"> <a class="nav-link" th:href="@{/emps}">//使用th标签获取 <svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="24" height="24" viewBox="0 0 24 24" fill="none" stroke="currentColor" stroke-width="2" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-linejoin="round" class="feather feather-users"> <path d="M17 21v-2a4 4 0 0 0-4-4H5a4 4 0 0 0-4 4v2"></path> <circle cx="9" cy="7" r="4"></circle> <path d="M23 21v-2a4 4 0 0 0-3-3.87"></path> <path d="M16 3.13a4 4 0 0 1 0 7.75"></path> </svg> 员工管理 </a> </li> -
编写请求对应的controller,处理
/emps请求,在controller包下,新建一个EmployeeController类@Controller public class LoginController { @RequestMapping("/user/login") // @ResponseBody public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username , @RequestParam("password") String password, Model model, HttpSession session){ if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(username)&&"123456".equals(password)){ session.setAttribute("loginUser",username); return "redirect:/main.html"; }else { model.addAttribute("msg","用户名或者密码错误"); return "index"; } } } -
重启主程序进行测试,登录到dashboard页面,再点击员工管理,成功跳转到 /emps
提取页面公共部分:
-
在
templates目录下新建一个***mons包,其中新建***mons.html用来放置公共页面代码,并且删除dashboard.html和list.html中顶部导航栏和侧边栏的代码 -
在dashboard.html和list.html中插入顶部导航栏和侧边栏的代码
<!--顶部导航栏--> <div th:replace="~{***mons/***mons::topbar}"></div> <div class="container-fluid"> <div class="row"> <!--传递参数给组件--> <div th:replace="~{***mons/***mons::sidebar}"></div> -
测试
添加点击高亮:
-
在
dashboard.html的侧边栏标签传递参数active为dashboard.html同样在
list.html的侧边栏标签传递参数active为list.html<div th:replace="~{***mons/***mons::sidebar(active='main.html')}"></div> -
然后我们在公共页面
***mons.html相应标签部分利用thymeleaf接收参数active,利用三元运算符判断决定是否高亮<a th:class="${active=='main.html'?'nav-link active':'nav-link'}" th:href="@{/index.html}"> <a th:class="${active=='list.html'?'nav-link active':'nav-link'}" th:href="@{/emps}"> -
测试
显示员工信息:
-
修改
list.html页面,显示后端的数据值<table class="table table-striped table-sm"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>lastName</th> <th>email</th> <th>gender</th> <th>department</th> <th>birth</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr th:each="emp:${emps}"> <td th:text="${emp.getId()}"></td> <td th:text="${emp.getLastName()}"></td> <td th:text="${emp.getEmail()}"></td> <td th:text="${emp.getGender()}=='0'?'女':'男'"></td> <td th:text="${emp.getDepartment.getDepartmentName()}"></td> <td th:text="${#dates.format(emp.getBirth(),'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}"></td> <td> <button class="btn btn-sm btn-primary">编辑</button> <button class="btn btn-sm btn-danger">删除</button> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> -
编写list方法
@Controller public class EmployeeController { @Autowired EmployeeDao employeeDao; @RequestMapping("/emps") public String list(Model model){ Collection<Employee> employees = employeeDao.getAll(); model.addAttribute("emps",employees); return "emp/list"; } } -
测试
添加员工:
-
在
add.html页面,当我们填写完信息,点击添加按钮,应该完成添加返回到list页面,展示新的员工信息;因此在add.html点击添加按钮的一瞬间,我们同样发起一个请求/add,与上述提交按钮发出的请求路径一样,但这里发出的是post请求<form th:action="@{/emp}" method="post"> <div class="form-group"> <label>LastName</label> <input type="text" name="lastName" class="form-control" placeholder="lastname:zsr"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Email</label> <input type="email" name="email" class="form-control" placeholder="email:xxxxx@qq.***"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Gender</label><br/> <div class="form-check form-check-inline"> <input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="1"> <label class="form-check-label">男</label> </div> <div class="form-check form-check-inline"> <input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="0"> <label class="form-check-label">女</label> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>department</label> <!--注意这里的name是department.id,因为传入的参数为id--> <select class="form-control" name="department.id"> <option th:each="department:${departments}" th:text="${department.getDepartmentName()}" th:value="${department.getId()}"></option> </select> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Birth</label> <!--springboot默认的日期格式为yy/MM/dd--> <input type="text" name="birth" class="form-control" placeholder="birth:yyyy/MM/dd"> </div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">添加</button> </form> -
编写对应的controller,同样在
EmployeeController中添加一个方法addEmp用来处理点击添加按钮的操作@GetMapping("/toAdd") public String toAddpage(Model model){ //获得有部门信息 Collection<Department> departments = departmentDao.getDepartment(); model.addAttribute("departments",departments); return "emp/add"; } @PostMapping("/emp") public String addEmp(Employee employee){ //添加 System.out.println(employee.toString()); employeeDao.save(employee); return "redirect:/emps"; } -
测试,进入添加页面,填写相关信息,注意日期格式默认为
yyyy/MM/dd
8.6、修改员工信息
-
list页面增加修改请求
<a class="btn btn-sm btn-primary" th:href="@{/emp/}+${emp.getId()}">编辑</a> -
编写toUpdateEmprestful风格接收参数接收参数并且返回数据信息
//去到员工的修改页面 @GetMapping("/emp/{id}") public String toUpdateEmp(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,Model model){ //查出原来的数据 Employee employee = employeeDao.getEmployeeById(id); model.addAttribute("emp",employee); //获得有部门信息 Collection<Department> departments = departmentDao.getDepartment(); model.addAttribute("departments",departments); return "emp/update"; } -
复制add页面修改为update页面
<form > <input type="hidden" name="id" th:value="${emp.getId()}"> <div class="form-group"> <label>LastName</label> <input th:value="${emp.getLastName()}" type="text" name="lastName" class="form-control" placeholder="海绵宝宝"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Email</label> <input th:value="${emp.getEmail()}" type="email" name="email" class="form-control" placeholder="1176244270@qq.***"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Gender</label><br> <div class="form-check form-check-inline"> <input th:checked="${emp.getGender()==1}" class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="1"> <label class="form-check-label">男</label> </div> </div> <div class="form-check form-check-inline"> <input th:checked="${emp.getGender()==0}" class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="0"> <label class="form-check-label">女</label> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>department</label> <select class="form-control" name="department.id"> <!--我们在controller接收的是一个Employee,所以我们需要提交的是其中的一个属性--> <option th:selected="${dept.getId()==emp.getDepartment().getId()}" th:each="dept:${departments}" th:text="${dept.getDepartmentName()}" th:value="${dept.getId()}"></option> </select> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Birth</label> <input th:value="${#dates.format(emp.getBirth(),'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}" type="text" name="birth" class="form-control" placeholder="2020-07-25 00:00:00"> </div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">修改</button> </form> -
edit页面编辑完成提交请求
<form th:action="@{/updateEmp}" method="post"> -
使用后端修改数据并且返回list页面
@PostMapping("/updateEmp") public String updateEmp(Employee employee){ employeeDao.save(employee); return "redirect:/emps"; } -
测试
8.7、删除员工信息
-
修改boton标签为a标签
<a class="btn btn-sm btn-danger" th:href="@{/delemp/}+${emp.getId()}">删除</a> -
编写对应的controller
//删除员工 @GetMapping("/delemp/{id}") public String delemp(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){ employeeDao.delete(id); return "redirect:/emps"; } -
测试
404页面
只需要在templates目录下新建一个error包,然后将404.html放入其中,报错SpringBoot就会自动找到这个页面
注销
-
在提取出来的公共
***mons页面,顶部导航栏处中的标签添加href属性,实现点击发起请求/user/logout<ul class="navbar-nav px-3"> <li class="nav-item text-nowrap"> <a class="nav-link" th:href="@{/user/logout}">注销</a> </li> </ul> -
编写对应的controller,处理点击
注销标签的请求,在LoginController中编写对应的方法,清除session,并重定向到首页//注销 @RequestMapping("/user/logout") public String logout(HttpSession session){ session.invalidate(); return "redirect:/index.html"; } -
测试
9、整合JDBC
9.1、SpringData简介
对于数据访问层,无论是 SQL(关系型数据库) 还是 NOSQL(非关系型数据库),Spring Boot 底层都是采用 Spring Data 的方式进行统一处理。
Spring Boot 底层都是采用 Spring Data 的方式进行统一处理各种数据库,Spring Data 也是 Spring 中与 Spring Boot、Spring Cloud 等齐名的知名项目。
Sping Data 官网:https://spring.io/projects/spring-data
数据库相关的启动器 :可以参考官方文档:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.2.5.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#using-boot-starter
9.2整合JDBC
数据库表:
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/`mybatis` /*!40100 DEFAULT
CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
USE `mybatis`;
CREATE TABLE `user`(
`id` INT(20) NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
`pwd` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(`id`)
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `user`(`id`,`name`,`pwd`) VALUES
(1,'狂神','123456'),
(2,'张三','abcdef'),
(3,'李四','987654');
写配置JDBC文件,application.xml:
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: root
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&userUniceode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
driver-class-name: ***.mysql.jdbc.Driver
JDBCTemplate
-
有了数据源(***.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource),然后可以拿到数据库连接(java.sql.Connection),有了连接,就可以使用原生的 JDBC 语句来操作数据库;
-
即使不使用第三方第数据库操作框架,如 MyBatis等,Spring 本身也对原生的JDBC 做了轻量级的封装,即JdbcTemplate。
-
数据库操作的所有 CRUD 方法都在 JdbcTemplate 中。
-
Spring Boot 不仅提供了默认的数据源,同时默认已经配置好了 JdbcTemplate 放在了容器中,程序员只需自己注入即可使用
-
JdbcTemplate 的自动配置是依赖 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc 包下的 JdbcTemplateConfiguration 类
JdbcTemplate主要提供以下几类方法:
execute方法:可以用于执行任何SQL语句,一般用于执行DDL语句;
update方法及batchUpdate方法:update方法用于执行新增、修改、删除等语句;batchUpdate方法用于执行批处理相关语句;
query方法及queryForXXX方法:用于执行查询相关语句;
call方法:用于执行存储过程、函数相关语句。
测试:
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot04DataApplicationTests {
//注入数据
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
void contextLoads() throws SQLException {
//查看默认数据源
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
//获得数据连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(dataSource);
//xxx Template : SpringBoot已经配置好了模板Bean, 拿来即用 crud
//关闭
connection.close();
}
}
**测试CRUD : **
@RestController
public class JDB***ontroller {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//查询数据库的所有信息
//没有实体类,数据库中的东西如何获取
@GetMapping("/userList")
public List<Map<String,Object>> userList(){
System.out.println("11");
String sql = "select * from user";
List<Map<String,Object>> List_map= jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql); //查询
System.out.println(List_map.toString());
return List_map;
}
//添加
@GetMapping("/addUser")
public String addUser(){
String sql = "insert into user(id,name,pwd) values(6,'高启强','1234567')" ;
jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
return "updateOK";
}
//修改
@GetMapping("/update/{id}")
public String update(@PathVariable("id") int id){
String sql = "update user set name = ?,pwd = ? where id ="+id;
//封装
Object[] object = new Object[2];
object[0] = "高起盛";
object[1] = "666";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,object);
return "updateOK";
}
//删除
@GetMapping("/del/{id}")
public String del(@PathVariable("id") int id){
String sql = "delete from user where id = ?" ;
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,id);
return "updateOK";
}
}
10、集成Druid
10.1、Druid简介
Java程序很大一部分要操作数据库,为了提高性能操作数据库的时候,又不得不使用数据库连接池。
Druid 是阿里巴巴开源平台上一个数据库连接池实现,结合了 C3P0、DBCP 等 DB 池的优点,同时加入了日志监控。
Druid 可以很好的监控 DB 池连接和 SQL 的执行情况,天生就是针对监控而生的 DB 连接池。
Druid已经在阿里巴巴部署了超过600个应用,经过一年多生产环境大规模部署的严苛考验。
Spring Boot 2.0 以上默认使用 Hikari 数据源,可以说 Hikari 与 Driud 都是当前 Java Web 上最优秀的数据源,我们来重点介绍 Spring Boot 如何集成 Druid 数据源,如何实现数据库监控。
Github地址:https://github.***/alibaba/druid/
***.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 基本配置参数如下:
参数详解:
DruidDataSource的使用、配置
https://mp.weixin.qq.***/s/wVAGOP1JdXZi5DMEsX1Aug
配置属性详解:
| 配置 | 缺省值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| name | 配置这个属性的意义在于,如果存在多个数据源,监控的时候可以通过名字来区分开来。如果没有配置,将会生成一个名字,格式是:“DataSource-” + System.identityHashCode(this).另外配置此属性至少在1.0.5版本中是不起作用的,强行设置name会出错 | |
| url | 连接数据库的url,不同数据库不一样。例如: mysql : jdbc:mysql://10.20.153.104:3306/druid2 oracle : jdbc:oracle:thin:@10.20.149.85:1521:o***auto |
|
| username | 连接数据库的用户名 | |
| password | 连接数据库的密码。如果你不希望密码直接写在配置文件中,可以使用ConfigFilter。详细看这里:https://github.***/alibaba/druid/wiki/%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8ConfigFilter | |
| driverClassName | 根据url自动识别 | 这一项可配可不配,如果不配置druid会根据url自动识别dbType,然后选择相应的driverClassName |
| nitialSize | 0 | 初始化时建立物理连接的个数。初始化发生在显示调用init方法,或者第一次getConnection时 |
| maxActive | 8 | 最大连接池数量 |
| maxIdle | 8 | 已经不再使用,配置了也没效果 |
| minIdle | 最小连接池数量 | |
| maxWait | 获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒。配置了maxWait之后,缺省启用公平锁,并发效率会有所下降,如果需要可以通过配置useUnfairLock属性为true使用非公平锁。 | |
| poolPreparedStatements | false | 是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache。PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,比如说oracle。在mysql下建议关闭。 |
| maxOpenPreparedStatements | -1 | 要启用PSCache,必须配置大于0,当大于0时,poolPreparedStatements自动触发修改为true。在Druid中,不会存在Oracle下PSCache占用内存过多的问题,可以把这个数值配置大一些,比如说100 |
| validationQuery | 用来检测连接是否有效的sql,要求是一个查询语句。如果validationQuery为null,testOnBorrow、testOnReturn、testWhileIdle都不会其作用。 | |
| validationQueryTimeout | 单位:秒,检测连接是否有效的超时时间。底层调用jdbc Statement对象的void setQueryTimeout(int seconds)方法 | |
| testOnBorrow | false | 申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能。 |
| testWhileIdle | false | 建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性。申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。 |
| timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis | 1分钟(1.0.14) | 有两个含义:1) Destroy线程会检测连接的间隔时间,如果连接空闲时间大于等于minEvictableIdleTimeMillis则关闭物理连接 2) testWhileIdle的判断依据,详细看testWhileIdle属性的说明 |
| numTestsPerEvictionRun | 不再使用,一个DruidDataSource只支持一个EvictionRun | |
| minEvictableIdleTimeMillis | 30分钟(1.0.14) | 连接保持空闲而不被驱逐的最长时间 |
| connectionInitSqls | 物理连接初始化的时候执行的sql | |
| exceptionSorter | 根据dbType自动识别 | 当数据库抛出一些不可恢复的异常时,抛弃连接 |
| filters | 属性类型是字符串,通过别名的方式配置扩展插件,常用的插件有: 监控统计用的filter:stat 日志用的filter:log4j 防御sql注入的filter:wall | |
| proxyFilters | 类型是List<***.alibaba.druid.filter.Filter>,如果同时配置了filters和proxyFilters,是组合关系,并非替换关系 |
10.2、配置数据源
-
添加上 Druid 数据源依赖。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.***/artifact/***.alibaba/druid --> <dependency> <groupId>***.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.10</version> </dependency> -
去配置Druid,配置自定义的数据源
spring: datasource: username: root password: root url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&userUniceode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 driver-class-name: ***.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver type: ***.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource -
设置数据源连接初始化大小、最大连接数、等待时间、最小连接数 等设置项;可以查看源码
#Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定 #druid 数据源专有配置 initialSize: 5 minIdle: 5 maxActive: 20 maxWait: 60000 timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000 validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL testWhileIdle: true testOnBorrow: false testOnReturn: false poolPreparedStatements: true #配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入 #如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority #则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.***/artifact/log4j/log4j filters: stat,wall,log4j maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20 useGlobalDataSourceStat: true connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500 -
Druid中包含log4j所以需要导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> -
为 DruidDataSource 绑定全局配置文件中的参数,再添加到容器中,而不再使用 Spring Boot 的自动生成了;我们需要 自己添加 DruidDataSource 组件到容器中,并绑定属性
@Configuration public class DruidConfig { @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") @Bean public DataSource druidDataSource() { return new DruidDataSource(); } }没有注解会404报错
-
Druid具有看监控功能,可以方便用户在web端看见后台的操作,配置后台监控和过滤器
@Configuration public class DruidConfig { @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") @Bean public DataSource druidDataSource() { return new DruidDataSource(); } //后台监控 // 配置 Druid 监控管理后台的Servlet; // 内置 Servlet 容器时没有web.xml文件,所以使用 Spring Boot 的注册 Servlet 方式 @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet() { ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*"); // 这些参数可以在 ***.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet // 的父类 ***.alibaba.druid.support.http.ResourceServlet 中找到 Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>(); initParams.put("loginUsername", "admin"); //后台管理界面的登录账号 initParams.put("loginPassword", "111111"); //后台管理界面的登录密码 // 后台允许谁可以访问 // initParams.put("allow", "localhost"):表示只有本机可以访问 // initParams.put("allow", ""):为空或者为null时,表示允许所有访问 initParams.put("allow", ""); // deny:Druid 后台拒绝谁访问 // initParams.put("kuangshen", "192.168.1.20");表示禁止此ip访问 // 设置初始化参数 bean.setInitParameters(initParams); return bean; } //过滤器 @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter(){ FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean(); bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter()); //可以过滤的请求 HashMap<String, String> initParameters = new HashMap<>(); initParameters.put("exclusions","*.js,*.css,/druid/*");//这些东西不进行统计 bean.setInitParameters(initParameters); return bean; } } -
测试:(http://localhost:8080/druid/login.html)
11、整合Mybatis
官方文档:http://mybatis.org/spring-boot-starter/mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure/
Maven仓库地址:Maven Repository: org.mybatis.spring.boot » mybatis-spring-boot-starter » 2.1.3 (mvnrepository.***)
-
导入依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.***/artifact/org.mybatis.spring.boot/mybatis-spring-boot-starter --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.1</version> </dependency> -
配置数据库连接信息(不变)
spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?userUnicode=true&useSSL=true&characterEncoding=utf8 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=***.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver -
测试数据库是否连接成功!
@SpringBootTest class Springboot05MybatisApplicationTests { @Autowired DataSource dataSource; @Test void contextLoads() throws SQLException { System.out.println(dataSource); System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection()); } } -
创建实体类,导入 Lombok!
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class User { private int id; private String name; private String pwd; } -
创建mapper目录以及对应的 Mapper 接口
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="***.hwt.springboot05mybatis.mapper.UserMapper"> <select id="queryUserList" resultType="User"> select * from user </select> <select id="queryUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="User"> select * from user where id = #{id} </select> <update id="update" parameterType="User" > update user set name=#{name},pwd=#{pwd} where id = #{id} </update> <insert id="addUser" parameterType="User"> insert into user(id,name,pwd) values (#{id},#{name},#{pwd}) </insert> <delete id="delete" parameterType="int"> delete from user where id = #{id} </delete> </mapper> -
.整合mybatis,让spring可以识别mappper
#整合mybatis mybatis.type-aliases-package=***.hwt.springboot05mybatis.pojo mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml -
编写controller测试
@RestController public class UserController { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @GetMapping("/query") public List<User> queryUserList(){ List<User> userList = userMapper.queryUserList(); for (User user : userList) { System.out.println(user); } return userList; } @GetMapping("/byid/{id}") public User queryUserById(@PathVariable("id") int id){ User user = userMapper.queryUserById(id); System.out.println(user); return user; } @GetMapping("/updata") public String updateUser(){ User user = new User(4,"高启强","6616"); if (userMapper.update(user)!=0){ return "ok"; } return "false"; } @GetMapping("/del/{id}") public String delete(@PathVariable("id") int id){ userMapper.delete(id); return "ok"; } @GetMapping("/add") public String add(){ User user = new User(4,"高启强","666"); if (userMapper.addUser(user)!=0){ return "ok"; } return "false"; } } -
测试
12、SpringSecurity(安全)
一个安全的框架,其实通过过滤器和拦截器也可以实现
官网介绍:Spring Security[官网地址](Spring Security)
shiro、SpringSecurity:很像,除了类不一样
12.1、简介
Spring Security是一个功能强大且高度可定制的身份验证和访问控制框架。它实际上是保护基于spring的应用程序的标准。
Spring Security是一个框架,侧重于为Java应用程序提供身份验证和授权。与所有Spring项目一样,Spring安全性的真正强大之处在于它可以轻松地扩展以满足定制需求
在用户认证方面,Spring Security 框架支持主流的认证方式,包括 HTTP 基本认证、HTTP 表单验证、HTTP 摘要认证、OpenID 和 LDAP 等。在用户授权方面,Spring Security 提供了基于角色的访问控制和访问控制列表(A***ess Control List,ACL),可以对应用中的领域对象进行细粒度的控制。
SpringBoot中的SpringSecurity依赖:
<!--security-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
记住几个类 :
- WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter:自定义Security策略
-
AuthenticationManagerBuilder:自定义认证策略
- @EnableWebSecurity:开启WebSecurity模式 @Enable开启某个模式
两个单词:en是认证,or是权限
- 认证方式:Authentication
权限:Authorization
12.2、配置页面的访问权限
-
配置Controller层测试是否都能访问
@Controller public class RouterController { @RequestMapping({"/","/index"}) public String index(){ return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/toLogin") public String toLogin(){ return "views/login"; } //可以实现公用 @RequestMapping("/level1/{id}") public String level(@PathVariable("id") int id){ return "views/level1/" +id; } @RequestMapping("/level2/{id}") public String level2(@PathVariable("id") int id){ return "views/level2/" +id; } @RequestMapping("/level3/{id}") public String level3(@PathVariable("id") int id){ return "views/level3/" +id; } } -
配置SecurityConfigure,
@EnableWebSecurity public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { //首页所有人可以访问,功能页只有对应权限的人才能访问 http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/").permitAll() .antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1") .antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2") .antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3"); } }测试发现除了首页之外别的页面全部都报错:
403权限不足
-
添加认证和授权
//认证,springboot 2.1x可以直接使用 //密码编码:PasswordEncoder() //在spring Secutiry 5.0+之后增加了很多加密方法 @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder()) .withUser("root").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("root")).roles("vip1","vip2","vip3") .and().withUser("admin").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("root")).roles("vip2","vip3") .and().withUser("user").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("root")).roles("vip1"); } -
测试
12.3、权限控制和注销
-
开启自动配置的注销的功能
@EnableWebSecurity public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { //授权 @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { //首页所有人可以访问,功能页只有对应权限的人才能访问 http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/").permitAll() .antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1") .antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2") .antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3"); //没有访问权限默认会到登录页面 http.formLogin(); http.logout();//注销,开启了注销功能 } -
在前端,增加一个注销的按钮,index.html 导航栏中
<a class="item" th:href="@{/logout}"> <i class="sign-out icon"></i> 注销 </a> -
测试一下,登录成功后点击注销,发现注销完毕会跳转到登录页面!
-
添加语句注销成功后,让他依旧可以跳转到首页
http.logout().logoutSu***essUrl("/");//注销,开启了注销功能 -
测试,注销完毕后,发现跳转到首页OK
-
增加新的需求:用户没有登录的时候,导航栏上只显示登录按钮,用户登录之后,导航栏可以显示登录的用户信息及注销按钮!还有就是,比如kuangshen这个用户,它只有 vip2,vip3功能,那么登录则只显示这两个功能,而vip1的功能菜单不显示!这个就是真实的网站情况了!该如何做呢?
我们需要结合thymeleaf中的一些功能
sec:authorize=“isAuthenticated()”:是否认证登录!来显示不同的页面
导入thymeleaf和security结合的Maven依赖:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.***/artifact/org.thymeleaf.extras/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity4 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5</artifactId> <version>3.0.4.RELEASE</version> </dependency> -
修改前端页面
导入命名空间
<html lang="en" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/extras/spring-security">修改导航栏增加认证判断
<!--登录注销--> <div class="right menu"> <!--如果未登录--> <div sec:authorize="!isAuthenticated()"> <a class="item" th:href="@{/login}"> <i class="address card icon"></i> 登录 </a> </div> <!--如果已登录--> <div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()"> <a class="item"> <i class="address card icon"></i> 用户名:<span sec:authentication="principal.username"></span> 角色:<span sec:authentication="principal.authorities"></span> </a> </div> <div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()"> <a class="item" th:href="@{/logout}"> <i class="address card icon"></i> 注销 </a> </div> </div>重启测试发现注销出现404
-
注销404了,就是因为它默认防止csrf跨站请求伪造,因为会产生安全问题,我们可以将请求 改为post表单提交,或者在spring security中关闭csrf功能;我们试试:在 配置中增 加
http.csrf().disable();http.csrf().disable();//关闭csrf功能:跨站请求伪造,默认只能通过post方式提交logout请求 -
测试:
12.4、记住我及首页定制
记住我:
-
开启记住我功能
http.rememberMe();//开启记住我功能 -
我们再次启动项目测试一下,发现登录页多了一个记住我功能,我们登录之后关闭 浏览器,然后重新打开浏览器访问,发现用户依旧存在!
浏览器的cookie
并且可以知道这个cookie的保存日期默认为14天
-
击注销的时候,可以发现,spring security 帮我们自动删除了这个 cookie
**结论:**登录成功后,将cookie发送给浏览器保存,以后登录带上这个cookie,只要通过检查就可以免登录了。如果点击注销,则会删除这个cookie
具体的原理我们在JavaWeb
首页定制:
-
登录页配置后面指定 loginpage
//没有访问权限默认会到登录页面 http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin"); -
然后前端也需要指向我们自己定义的 login请求
<!--如果登录,就显示用户名和注销--> <div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()"> <a class="item" th:href="@{/logout}"> <!--从授权那里获取name--> 用户名:<span sec:authentication="name"></span> 角色:<span sec:authentication="principal.authorities"></span> </a> </div> -
我们登录,需要将这些信息发送到哪里,我们也需要配置,login.html 配置提交请求及方式,方式必须为post:
-
修改访问的页面和接受数据
http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin").usernameParameter("user").passwordParameter("pwd").loginProcessingUrl("/login");
- 添加前端登录页面记住我
<div class="field">
<input type="checkbox" name="remember"> 记住我
</div>
- hou端接收数据
http.rememberMe().rememberMeParameter("remember");//开启记住我功能
13、Shiro
13.1概述
简介
Apache Shiro是一个强大且易用的Java安全框架
可以完成身份验证、授权、密码和会话管理
Shiro 不仅可以用在 JavaSE 环境中,也可以用在 JavaEE 环境中
官网: http://shiro.apache.org/
功能
-
Authentication:身份认证/登录,验证用户是不是拥有相应的身份;
-
Authorization:授权,即权限验证,验证某个已认证的用户是否拥有某个权限;即判断用户是否能做事情,常见的如:验证某个用户是否拥有某个角色。或者细粒度的验证某个用户对某个资源是否具有某个权限;
-
Session Manager:会话管理,即用户登录后就是一次会话,在没有退出之前,它的所有信息都在会话中;会话可以是普通JavaSE环境的,也可以是如Web环境的;
-
Cryptography:加密,保护数据的安全性,如密码加密存储到数据库,而不是明文存储;
-
Web Support:Web支持,可以非常容易的集成到Web环境;
-
Caching:缓存,比如用户登录后,其用户信息、拥有的角色/权限不必每次去查,这样可以提高效率;
-
Concurrency:shiro支持多线程应用的并发验证,即如在一个线程中开启另一个线程,能把权限自动传播过去;
-
Testing:提供测试支持;
-
Run As:允许一个用户假装为另一个用户(如果他们允许)的身份进行访问;
-
Remember Me:记住我,这个是非常常见的功能,即一次登录后,下次再来的话不用登录了。
从外部看
应用代码直接交互的对象是Subject,也就是说Shiro的对外API核心就是Subject;其每个API的含义:
-
Subject:主体,代表了当前“用户”,这个用户不一定是一个具体的人,与当前应用交互的任何东西都是Subject,如网络爬虫,机器人等;即一个抽象概念;所有Subject都绑定到SecurityManager,与Subject的所有交互都会委托给SecurityManager;可以把Subject认为是一个门面;SecurityManager才是实际的执行者;
-
SecurityManager:安全管理器;即所有与安全有关的操作都会与SecurityManager交互;且它管理着所有Subject;可以看出它是Shiro的核心,它负责与后边介绍的其他组件进行交互,如果学习过SpringMVC,你可以把它看成DispatcherServlet前端控制器;
-
**Realm:**域,Shiro从从Realm获取安全数据(如用户、角色、权限),就是说SecurityManager要验证用户身份,那么它需要从Realm获取相应的用户进行比较以确定用户身份是否合法;也需要从Realm得到用户相应的角色/权限进行验证用户是否能进行操作;可以把Realm看成DataSource,即安全数据源。
-
也就是说对于我们而言,最简单的一个Shiro应用:
-
应用代码通过Subject来进行认证和授权,而Subject又委托给SecurityManager;
我们需要给Shiro的SecurityManager注入Realm,从而让SecurityManager能得到合法的用户及其权限进行判断。
从以上也可以看出,Shiro不提供维护用户/权限,而是通过Realm让开发人员自己注入
内部:
- Subject:任何可以与应用交互的“用户”;
- SecurityManager:相当于SpringMVC中的DispatcherServlet;是Shiro的心脏;所有具体的交互都通过SecurityManager进行控制;它管理着所有Subject、且负责进行认证、授权、会话及缓存的管理。
- Authenticator:负责Subject 认证,是一个扩展点,可以自定义实现;可以使用认证策略(Authentication Strategy),即什么情况下算用户认证通过了;
- Authorizer:授权器、即访问控制器,用来决定主体是否有权限进行相应的操作;即控制着用户能访问应用中的哪些功能;
- Realm:可以有1 个或多个Realm,可以认为是安全实体数据源,即用于获取安全实体的;可以是JDBC 实现,也可以是内存实现等等;由用户提供;所以一般在应用中都需要实现自己的Realm;
- SessionManager:管理Session 生命周期的组件;而Shiro并不仅仅可以用在Web 环境,也可以用在如普通的JavaSE环境
- CacheManager:缓存控制器,来管理如用户、角色、权限等的缓存的;因为这些数据基本上很少改变,放到缓存中后可以提高访问的性能
- Cryptography:密码模块,Shiro提高了一些常见的加密组件用于如密码加密/解密。
认证流程: 用户 提交 身份信息、凭证信息 封装成 令牌 交由 安全管理器 认证
13.2、快速入手
-
新建一个 Maven 工程,删除其 src 目录,将其作为父工程
-
在父工程中新建一个 Maven 模块
-
复制快速入门案例 POM.xml 文件中的依赖 (版本号自选)
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId> <version>1.5.3</version> </dependency> <!-- configure logging --> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId> <version>1.7.26</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> <version>1.7.26</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> </dependencies>把快速入门案例中的 resource 下的
log4j.properties复制下来log4j.rootLogger=INFO, stdout log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %p [%c] - %m %n # General Apache libraries log4j.logger.org.apache=WARN # Spring log4j.logger.org.springframework=WARN # Default Shiro logging log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro=INFO # Disable verbose logging log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.util.ThreadContext=WARN log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCache=WARN -
复制一下
shiro.ini文件[users] # user 'root' with password 'secret' and the 'admin' role root = secret, admin # user 'guest' with the password 'guest' and the 'guest' role guest = guest, guest # user 'presidentskroob' with password '12345' ("That's the same ***bination on # my luggage!!!" ;)), and role 'president' presidentskroob = 12345, president # user 'darkhelmet' with password 'ludicrousspeed' and roles 'darklord' and 'schwartz' darkhelmet = ludicrousspeed, darklord, schwartz # user 'lonestarr' with password 'vespa' and roles 'goodguy' and 'schwartz' lonestarr = vespa, goodguy, schwartz # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Roles with assigned permissions # # Each line conforms to the format defined in the # org.apache.shiro.realm.text.TextConfigurationRealm#setRoleDefinitions JavaDoc # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- [roles] # 'admin' role has all permissions, indicated by the wildcard '*' admin = * # The 'schwartz' role can do anything (*) with any lightsaber: schwartz = lightsaber:* # The 'goodguy' role is allowed to 'drive' (action) the winnebago (type) with # license plate 'eagle5' (instance specific id) goodguy = winnebago:drive:eagle5下载ini插件,如果在setting中无法下载,就去官网下载对应版本的然后导入
-
导入quickstart.java
-
执行一下main方法:
2023-03-12 01:23:44,155 INFO [org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.AbstractValidatingSessionManager] - Enabling session validation scheduler... 2023-03-12 01:23:44,755 INFO [Quickstart] - Retrieved the correct value! [aValue] 2023-03-12 01:23:44,756 INFO [Quickstart] - User [lonestarr] logged in su***essfully. 2023-03-12 01:23:44,756 INFO [Quickstart] - May the Schwartz be with you! 2023-03-12 01:23:44,757 INFO [Quickstart] - You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely. 2023-03-12 01:23:44,757 INFO [Quickstart] - You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. Here are the keys - have fun!
13.4、SpringBoot整合Shiro环境搭建
测试环境搭建:
-
新建一个项目或模块
-
导入依赖
<!-- thymeleaf模板--> <dependency> <groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-java8time</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> -
新建一个controller类测试运行环境
@Controller public class MyController { @RequestMapping({"/index","/"}) public String toIndex(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","hello,shiro"); return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/user/add") public String add(){ return "user/add"; } @RequestMapping("/user/update") public String update(){ return "user/update"; } } -
分别在config包下新建
UserRealm和ShiroConfig两个类//自定义UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { //授权 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { System.out.println("执行了=>授权doGetAuthorizationInfo"); return null; } //认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("执行力=>认证doGetAuthenticationInfo"); return null; } }@Configuration public class ShiroConfig { //ShiroFilterFactoryBean @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager")DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){ ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); //设置安全管理器 bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager); return bean; } //DefaultWebSecurityManager @Bean(name="securityManager") public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm){ DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); //关联UserRealm securityManager.setRealm(userRealm); return securityManager; } //创建realm对象 ,需要自定义 @Bean public UserRealm userRealm(){ return new UserRealm(); } } -
在templates包下新建user包并且新建add.html和update.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>add</h1> </body> </html><!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>update</h1> </body> </html>并且在index.html中添加跳转超链接
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:shiro="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-shiro"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>首页</h1> <!--/*@thymesVar id="msg" type="co m.hwt.controller.MyController"*/--> <p th:text="${msg}"></p> <a th:href="@{/user/add}">add</a> | <a th:href="@{/user/update}">update</a> </body> </html> -
测试
13.5、Shiro实现登录拦截
-
编写登录页面login.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>登录</title> </head> <body> <h1>登录</h1> <hr> <form action=""> <p>用户名:<input type="text" name="username"></p> <p>密码:<input type="text" name="password"></p> <p><input type="submit"></p> </form> </body> </html> -
在controller中添加路径跳转
@RequestMapping("/toLogin") public String toLogin(){ return "login"; } -
在
ShiroConfig中的getShiroFilterFactoryBean方法中添加如下配置//设置没有权限进入登录页面 bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin"); -
测试点击update跳转到了login页面
13.6、Shiro实现用户认证
实现用户认证需要去realm类的认证方法中去配置
这里我们先把用户名和密码写死,实际中是要去数据库中去取的
-
在
MyController中编写用户提交表单之后处理@RequestMapping("/login") public String login(String username ,String password,Model model){ //获取当前用户 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //封装用户的登录数据 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password); try { subject.login(token);//执行登录方法,没有异常就登录成功了 return "index"; } catch (UnknownA***ountException e) { //用户名不存在 model.addAttribute("msg","用户名错误"); return "login"; } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) { //密码错误 model.addAttribute("msg","密码错误"); return "login"; } } -
ogin.html的修改
<body> <h1>登录</h1> <hr> <!--/*@thymesVar id="msg" type="***.hwt.controller.MyController"*/--> <p th:text="${msg}" style="color: red"></p> <form th:action="@{/login}"> <p>用户名:<input type="text" name="username"></p> <p>密码:<input type="text" name="password"></p> <p><input type="submit"></p> </form> </body> -
UserRealm的认证方法中添加假信息并且认证
//认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("执行力=>认证doGetAuthenticationInfo"); //用户 String name = "root"; String password = "root"; UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token; if (!userToken.getUsername().equals(name)){ return null; //抛出异常 UnknownA***ountException } //密码认证"shiro做 return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",password,""); } -
测试:用户输入登录信息
13.7、Shiro整合mybatis
-
导入相关依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>***.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.23</version> </dependency> <!--引入mybatis,这是MyBatis官方提供的适配spring Boot的,而不是spring Boot自己的--> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.3</version> </dependency> -
编写配置文件
spring: datasource: username: root password: root url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&userUniceode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=UTC driver-class-name: ***.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver type: ***.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定 #druid 数据源专有配置 initialSize: 5 minIdle: 5 maxActive: 20 maxWait: 60000 timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000 validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL testWhileIdle: true testOnBorrow: false testOnReturn: false poolPreparedStatements: true #配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入 #如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority #则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.***/artifact/log4j/log4j filters: stat,wall,log4j maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20 useGlobalDataSourceStat: true connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500 -
编写实体类
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class User { private int id; private String name; private String pwd; } -
编写mapper和xml文件
@Repository @Mapper public interface UserMapper { public User queryUserByName(String name); }<mapper namespace="***.hwt.mapper.UserMapper"> <select id="queryUserByName" resultType="User" parameterType="String"> select * from user where name=#{name} </select> </mapper> -
service和service的实现类
public interface UserService { public User queryUserByName(String name); }@Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired UserMapper userMapper; @Override public User queryUserByName(String name) { return userMapper.queryUserByName(name); } } -
测试类中测试
@SpringBootTest class ShiroSpringbootApplicationTests { @Autowired UserService userService; @Test void contextLoads() { System.out.println(userService.queryUserByName("root")); } } -
Realm中获取数据库数据并且与前端传值进行比对
//认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("执行力=>认证doGetAuthenticationInfo"); //使用真实数据 UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordToken)token; User user = userService.queryUserByName(userToken.getUsername()); if(user==null){ return null; } return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",user.getPwd(),""); }
13.8、Shiro请求授权的实现
ShiroConfig.java中,添加代码,注意要添加在(顺序)
filterMap.put("/user/add","perms[user:add]");
正常的是要访问无权限页面的
现在去UserRealm中给添加权限
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("执行了授权方法");
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
info.addStringPermission("user:add");
return info;
}
现在测试发现用户就有add权限了
怎样在数据库层面实现呢
首先添加一个权限字段perms
之后在类中新建这个字段
在UserRealm中为用户添加基于数据库的授权
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("执行了=>授权doGetAuthorizationInfo");
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
//拿到当前用户信息
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
User currentUser = (User) subject.getPrincipal();//拿到数据库权限
info.addStringPermission(currentUser.getPerms());
return info;
}
13.9、Shiro和thymeleaf整合
-
导入shrio和thymeleaf结合的依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.***/artifact/***.github.theborakompanioni/thymeleaf-extras-shiro --> <dependency> <groupId>***.github.theborakompanioni</groupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-shiro</artifactId> <version>2.0.0</version> </dependency> -
在UserRealm类的认证登录中把session中放入user
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); Session session = subject.getSession(); session.setAttribute("loginUser",user); -
前端页面编写标签了,之前在security中用到的是sec,这里用的shiro
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:shiro="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-shiro"> -
修改前端页面
<div> <div th:if="${session.loginUser==null}"> <a th:href="@{/toLogin}">登录</a> </div> <p th:text="${msg}"></p> <div shiro:hasPermission="user:add"> <a th:href="@{/user/add}">add</a> </div> <div shiro:hasPermission="user:update"> <a th:href="@{/user/update}">update</a> </div> </div> -
测试:登录后只显示当前啊用户有权限的操作
14、Swagger
14.1、Swagger简介
前后端分离
- 前端 -> 前端控制层、视图层
- 伪造后端数据,json已经存在,不需要后端,前端已经能跑起来
- 后端 -> 后端控制层、服务层、数据访问层
- 前后端通过API进行交互
- 前后端相对独立且松耦合
- 前后端可以部署在不同的服务器上
产生的问题
- 前后端集成,前端或者后端无法做到“及时协商,尽早解决”,最终导致问题集中爆发
解决方案
- 首先定义schema [ 计划的提纲 ],并实时跟踪最新的API,降低集成风险
- 早些年制定word计划文档
- 前后端分离:前端测试后端接口:postman
后端提供接口,需要实时更新最新的消息及改动!
Swagger
- 号称世界上最流行的API框架
- Restful Api 文档在线自动生成器 => API 文档 与API 定义同步更新
- 直接运行,在线测试API接口(其实就是controller requsetmapping)
- 支持多种语言 (如:Java,PHP等)
- 官网:https://swagger.io/
14.2、SpringBoot集成Swagger
14.2.1、环境搭建
SpringBoot集成Swagger => springfox,两个jar包
- Springfox-swagger2
- swagger-springmvc
使用Swagger
要求:jdk 1.8 + 否则swagger2无法运行
-
新建一个springBoot-web项目
-
添加maven依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.***/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId> <version>2.9.2</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.***/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId> <version>2.9.2</version> </dependency> -
编写HelloController
@RestController public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ return "hello"; } } -
编写一个配置类SwaggerConfig类配置Swagger
@Configuration @EnableSwagger2 public class SwaggerConfig { } -
访问测试 :http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html ,可以看到swagger的界面;
14.2.2配置Swagger
-
Swagger实例Bean是Docket,所以通过配置Docket实例来配置Swagger,通过Docket对象接管了原来默认的配置
//配置Swagger文档信息=apiInfo private ApiInfo apiInfo() { Contact contact = new Contact("联系人名字", "http://xxx.xxx.***/联系人访问链接", "联系人邮箱"); return new ApiInfo( "Swagger", // 标题 "配置Swagger", // 描述 "v1.0", // 版本 "https://swagger.io/", // 组织链接 contact, // 联系人信息 "Apach 2.0 许可", // 许可 "许可链接", // 许可连接 new ArrayList<>()// 扩展 ); } -
通过apiInfo()属性配置文档信息
@Bean //配置docket以配置Swagger具体参数 public Docket docket() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()); } -
Docket 实例关联上 apiInfo()
14.2.3配置扫描接口
构建Docket时通过select()方法配置怎么扫描接口。
@Bean //配置docket以配置Swagger具体参数
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("***.hwt.swagger.controller"))
.build();
}
空行处可以使用的全部参数
//RequestHandlerSelectors配置接口扫面的方式
//basePackage指定扫描的包
//any() // 扫描所有,项目中的所有接口都会被扫描到
//none() // 不扫描接口
//通过方法上的注解扫描,如withMethodAnnotation(GetMapping.class)只扫描get请求
//withMethodAnnotation(final Class<? extends Annotation> annotation)
//通过类上的注解扫描,如.withClassAnnotation(Controller.class)只扫描有controller注解的类中的接口
//withClassAnnotation(final Class<? extends Annotation> annotation)
//basePackage(final String basePackage) // 根据包路径扫描接口
//paths(PathSelectors.ant(“/kuang/**”)) //过滤什么路径:过滤/kuang下的所有路径
14.2.4配置Swagger开关
通过enable是否启动swagger 如果是false 则swagger不能在浏览器中使用
@Bean //配置docket以配置Swagger具体参数
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(false)//enable是否启动swagger 如果是false 则swagger不能在浏览器中使用
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("***.hwt.swagger.controller"))
.build();
}
如何动态配置当项目处于test、dev环境时显示swagger,处于prod时不显示?
- 判断是不是生产环境flag=false
- 注入enable(flag)
分别配置pro和dev的端口号为8081和8082
然后在docket类中进行判断
@Bean //配置docket以配置Swagger具体参数
public Docket docket(Environment environment) {
// 设置要是示的Swagger环境
Profiles profiles = Profiles.of("dev","test");
// 获取项目的环境
// 通过environment.a***eptsProfiles 判断是否处于自己设定的环境当中
boolean flag = environment.a***eptsProfiles(profiles);
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(flag)//enable是否启动swagger 如果是false 则swagger不能在浏览器中使用
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("***.hwt.swagger.controller"))
.build();
}
14.2.5配置API分组
多个分组:只需要多个Docket实例即可
@Bean
public Docket docket1(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("a");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("b");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket3(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("c");
}
测试:
14.2.6实体配置
-
新建一个实体类
public class User { public String username; public String password; } -
实体在请求接口的返回值上(即使是泛型),都能映射到实体项中:
@PostMapping(value = "/user") public User user(){ return new User(); } -
增加注释
@ApiModel("用户实体") public class User { @ApiModelProperty("用户名") public String username; @ApiModelProperty("密码") public String password; }注:并不是因为@ApiModel这个注解让实体显示在这里了,而是只要出现在接口方法的返回值上的实体都会显示在这里,而@ApiModel和@ApiModelProperty这两个注解只是为实体添加注释的。
@ApiModel为类添加注释
@ApiModelProperty为类属性添加注释
14.3常用注解
Swagger的所有注解定义在io.swagger.annotations包下
下面列一些经常用到的,未列举出来的可以另行查阅说明:
| Swagger注解 | 简单说明 |
|---|---|
| @Api(tags = “xxx模块说明”) | 作用在模块类上 |
| @ApiOperation(“xxx接口说明”) | 作用在接口方法上 |
| @ApiModel(“xxxPOJO说明”) | 作用在模型类上:如VO、BO |
| @ApiModelProperty(value = “xxx属性说明”,hidden = true) | 作用在类方法和属性上,hidden设置为true可以隐藏该属性 |
| @ApiParam(“xxx参数说明”) | 作用在参数、方法和字段上,类似@ApiModelProperty |
给请求的接口配置一些注释
//Operation接口,不是放在类上是方法
@ApiOperation("get测试类")
@GetMapping("/t2")
public String t1(@ApiParam("这个名字会被返回")String username){
return username;
}
@ApiOperation("post测试类")
@PostMapping("/t2")
public String t2(@ApiParam("这个名字会被返回")String name){
int i = 2/0;
return name;
}
这样的话,可以给一些比较难理解的属性或者接口,增加一些配置信息,让人更容易阅读!
相较于传统的Postman或Curl方式测试接口,使用swagger简直就是傻瓜式操作,不需要额外说明文档(写得好本身就是文档)而且更不容易出错,只需要录入数据然后点击Execute,如果再配合自动化框架,可以说基本就不需要人为操作了。
Swagger是个优秀的工具,现在国内已经有很多的中小型互联网公司都在使用它,相较于传统的要先出Word接口文档再测试的方式,显然这样也更符合现在的快速迭代开发行情。当然了,提醒下大家在正式环境要记得关闭Swagger,一来出于安全考虑二来也可以节省运行时内存。
15、任务
15.1异步任务
所谓异步,在某些功能实现时可能要花费一定的时间,但是为了不影响客户端的体验,选择异步执行
-
创建一个service
@Service public class AsynService { public void hello(){ try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("数据正在处理。。。"); } } -
创建一个controller
@RestController public class AsynController { @Autowired AsynService asynService; @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ asynService.hello(); return "ok"; } } -
测试,在执行是等待三秒才执行
-
实现异步需要告诉sprng这个方法是异步的,在方法加上注解
@RestController public class AsynController { @Autowired AsynService asynService; @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ asynService.hello(); return "ok"; } } -
在SpringBoot主程序开启异步注解的功能
@EnableAsync//开启异步注解功能 @SpringBootApplication public class Springboot09TestApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Springboot09TestApplication.class, args); } } -
测试页面先出来 3秒后才打印数据正在处理。。。
15.2邮件任务
邮件发送,在我们的日常开发中,也非常的多,Springboot也帮我们做了支持
- 邮件发送需要引入spring-boot-start-mail
- SpringBoot 自动配置MailSenderAutoConfiguration
- 定义MailProperties内容,配置在application.yml中
- 自动装配JavaMailSender
- 测试邮件发送
-
导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId> </dependency> -
设置自己的邮箱
spring.mail.username=xxxxxxxx@qq.*** spring.mail.password=xxxxxxxxxxxx spring.mail.host=smtp.qq.*** #开启加密验证 spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.ssl.enable=true -
发送简单邮件
@Test void contextLoads() { SimpleMailMessage mailMessage = new SimpleMailMessage(); mailMessage.setSubject("测试"); mailMessage.setText("6666"); mailMessage.setTo("xxxxxxxx@qq.***"); mailMessage.setFrom("xxxxxxxxx@qq.***"); mailSender.send(mailMessage); } -
发送发杂邮件(带附件的文件)
@Test void contextLoads2() throws MessagingException { //一个复杂邮件 MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage(); //组装 MimeMessageHelper helper =new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage,true); helper.setSubject("测试"); helper.setText("6666"); //附件 helper.addAttachment("1.jpg",new File("D:\\1.jpg")); helper.addAttachment("2.jpg",new File("D:\\1.jpg")); helper.setTo("2813068665@qq.***"); helper.setFrom("2813068665@qq.***"); mailSender.send(mimeMessage); }
15.3定时任务
项目开发中经常需要执行一些定时任务,比如需要在每天凌晨的时候,分析一次前一天的日志信息,Spring为我们提供了异步执行任务调度的方式,提供了两个接口。
- TaskExecutor接口 任务调度者
- TaskScheduler接口 任务执行者
两个注解:
- @EnableScheduling 开启定时功能的注释
- @Scheduled 什么时候执行
-
定时功能注解在springboot主方法中开启定时功能注解
@EnableAsync//开启异步注解功能 @EnableScheduling//开启定时功能的注解 @SpringBootApplication public class Springboot09TestApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Springboot09TestApplication.class, args); } } -
开启注解并且使用使用cron表达式操作定时任务
@Service public class ScheduledService { //在一个特定的时间执行这个方法 Timer // cron 表达式~ // 秒 分 时 日 月 周几 @Scheduled(cron = "0 47 14 * * ?") public void hello(){ System.out.println("hello,你被执行了"); } } -
测试
cron表达式:https://www.***blogs.***/javahr/p/8318728.html
16、分布式 Dubbo+Zooker
16.1、什么是分布式系统?
在《分布式系统原理与范型》一书中有如下定义:“分布式系统是若干独立计算机的集合,这些计算机对于用户来说就像单个相关系统”;
分布式系统是由一组通过网络进行通信、为了完成共同的任务而协调工作的计算机节点组成的系统。分布式系统的出现是为了用廉价的、普通的机器完成单个计算机无法完成的计算、存储任务。其目的是利用更多的机器,处理更多的数据。
分布式系统(distributed system)是建立在网络之上的软件系统。
首先需要明确的是,只有当单个节点的处理能力无法满足日益增长的计算、存储任务的时候,且硬件的提升(加内存、加磁盘、使用更好的CPU)高昂到得不偿失的时候,应用程序也不能进一步优化的时候,我们才需要考虑分布式系统。因为,分布式系统要解决的问题本身就是和单机系统一样的,而由于分布式系统多节点、通过网络通信的拓扑结构,会引入很多单机系统没有的问题,为了解决这些问题又会引入更多的机制、协议,带来更多的问题。。。
RPC:
RPC【Remote Procedure Call】是指远程过程调用,是一种进程间通信方式,他是一种技术的思想,而不是规范。它允许程序调用另一个地址空间(通常是共享网络的另一台机器上)的过程或函数,而不用程序员显式编码这个远程调用的细节。即程序员无论是调用本地的还是远程的函数,本质上编写的调用代码基本相同。
也就是说两台服务器A,B,一个应用部署在A服务器上,想要调用B服务器上应用提供的函数/方法,由于不在一个内存空间,不能直接调用,需要通过网络来表达调用的语义和传达调用的数据。为什么要用RPC呢?就是无法在一个进程内,甚至一个计算机内通过本地调用的方式完成的需求,比如不同的系统间的通讯,甚至不同的组织间的通讯,由于计算能力需要横向扩展,需要在多台机器组成的集群上部署应用。RPC就是要像调用本地的函数一样去调远程函数;
RPC两个核心模块:通讯,序列化。
Dubbo:
Apache Dubbo |ˈdʌbəʊ| 是一款高性能、轻量级的开源Java RPC框架,它提供了三大核心能力:面向接口的远程方法调用,智能容错和负载均衡,以及服务自动注册和发现。
Dubbo 作为一款微服务框架,最重要的是向用户提供跨进程的 RPC 远程调用能力。如上图所示,Dubbo 的服务消费者(Consumer)通过一系列的工作将请求发送给服务提供者(Provider)。
为了实现这样一个目标,Dubbo 引入了注册中心(Registry)组件,通过注册中心,服务消费者可以感知到服务提供者的连接方式,从而将请求发送给正确的服务提供者。
-
服务提供者(Provider):暴露服务的服务提供方,服务提供者在启动时,向注册中心注册自己提供的服务。
-
服务消费者(Consumer):调用远程服务的服务消费方,服务消费者在启动时,向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务,服务消费者,从提供者地址列表中,基于软负载均衡算法,选一台提供者进行调用,如果调用失败,再选另一台调用。
-
注册中心(Registry):注册中心返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者,如果有变更,注册中心将基于长连接推送变更数据给消费者
-
监控中心(Monitor):服务消费者和提供者,在内存中累计调用次数和调用时间,定时每分钟发送一次统计数据到监控中心
调用关系说明
l 服务容器负责启动,加载,运行服务提供者。
l 服务提供者在启动时,向注册中心注册自己提供的服务。
l 服务消费者在启动时,向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务。
l 注册中心返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者,如果有变更,注册中心将基于长连接推送变更数据给消费者。
l 服务消费者,从提供者地址列表中,基于软负载均衡算法,选一台提供者进行调用,如果调用失败,再选另一台调用。
l 服务消费者和提供者,在内存中累计调用次数和调用时间,定时每分钟发送一次统计数据到监控中心。
16.2、windows下安装zookeeper
- 下载zookeeper :地址, 我们下载3.4.14 , 最新版!解压zookeeper
- 运行/bin/zkServer.cmd ,初次运行会报错,没有zoo.cfg配置文件;
可能碰到的问题:闪退
解决方案:编辑zkServer.cmd文件末尾添加pause 。这样运行出错就不会退出,会提示错误信息,方便 找到原因。
-
修改zoo.cfg配置文件
将conf文件夹下面的zoo_sample.cfg复制一份改名为zoo.cfg即可。
注意几个重要位置:
dataDir=./ 临时数据存储的目录(可写相对路径)
clientPort=2181 zookeeper的端口号
修改完成后再次启动zookeeper
-
启动zkCli.cmd测试
ls/ :列出列出zookeeper根下保存的所有节点
create –e /hwt 666:创建一个hwt节点,值为666
16.3、window下安装dubbo-admin
dubbo本身不是一个服务软件。它其实就是一个jar包,能够帮你的java程序连接到zookeeper,并利用zookeeper消费、提供服务。
但是为了让用户更好的管理监控众多的dubbo服务,官方提供了一个可视化的监控程序dubbo-admin,不过这个监控即使不装也不影响使用。
安装:
-
下载:https://github.***/apache/dubbo-admin/tree/master
-
解压到环境目录
-
修改 dubbo-admin\src\main\resources \application.properties 指定zookeeper地址
server.port=7001 spring.velocity.cache=false spring.velocity.charset=UTF-8 spring.velocity.layout-url=/templates/default.vm spring.messages.fallback-to-system-locale=false spring.messages.basename=i18n/message spring.root.password=root spring.guest.password=guest dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 -
在项目目录下打包dubbo-admin
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true -
执行 dubbo-admin\target 下的dubbo-admin-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
java -jar dubbo-admin-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar -
执行完毕,我们去访问一下 http://localhost:7001/ , 这时候我们需要输入登录账户和密码,我们都是默认的root-root;
登录成功后,查看界面
17、SpringBoot + Dubbo + zookeeper
17.1、框架搭建:
-
启动zookeeper !
-
IDEA创建一个空项目;
-
创建一个模块,实现服务提供者:provider-server , 选择web依赖即可
-
项目创建完毕,我们写一个服务,比如卖票的服务;
编写接口
public interface TicketService { public String getTicket(); }编写实现类
@Service //将服务发布出去 @***ponent //放在容器中 public class TicketServiceImpl implements TicketService{ @Override public String getTicket() { return "SpringBoot + Dubbo + zookeeper"; } } -
创建一新的个模块,实现服务消费者:consumer-server , 选择web依赖即可
-
.项目创建完毕,我们写一个服务,比如用户的服务;
package ***.guo.consumer.service; public class UserService { //我们需要去拿去注册中心的服务 }
17.2、服务提供者:
-
将服务提供者注册到注册中心,我们需要整合Dubbo和zookeeper,所以需要导包
我们从dubbo官网进入github,看下方的帮助文档,找到dubbo-springboot,找到依赖包
<!-- Dubbo Spring Boot Starter --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId> <artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.7.3</version> </dependency>zookeeper的包我们去maven仓库下载,zkclient;
<!-- https://mvnrepository.***/artifact/***.github.sgroschupf/zkclient --> <dependency> <groupId>***.github.sgroschupf</groupId> <artifactId>zkclient</artifactId> <version>0.1</version> </dependency>【新版的坑】zookeeper及其依赖包,解决日志冲突,还需要剔除日志依赖;
<!-- 引入zookeeper --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId> <artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId> <version>2.12.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId> <artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId> <version>2.12.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId> <artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId> <version>3.4.14</version> <!--排除这个slf4j-log4j12--> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> -
在springboot配置文件中配置dubbo相关属性!
#当前应用名字 dubbo.application.name=provider-server #注册中心地址 dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 #扫描指定包下服务 dubbo.scan.base-packages=***.hwt.service -
在service的实现类中配置服务注解,发布服务!注意导包问题,因为这里的Service注解需要导入的是dubbo中的注解,而不是spring的注解,所以要把其注入就要用***po***,不过最新版本的好像已经解决这个问题:一个新的注解@DubboService
@Service //将服务发布出去 @***ponent //放在容器中 public class TicketServiceImpl implements TicketService{ @Override public String getTicket() { return "SpringBoot + Dubbo + zookeeper"; } } -
测试运行,需要提前打开zookeepr服务
-
可以看到服务已经存在了
逻辑理解 :应用启动起来,dubbo就会扫描指定的包下带有@***ponent注解的服务,将它发布在指定的注册中心中!
17.3、服务消费者
-
导入依赖,和之前的依赖一样;
<!--dubbo--> <!-- Dubbo Spring Boot Starter --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId> <artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.7.3</version> </dependency> <!--zookeeper--> <!-- https://mvnrepository.***/artifact/***.github.sgroschupf/zkclient --> <dependency> <groupId>***.github.sgroschupf</groupId> <artifactId>zkclient</artifactId> <version>0.1</version> </dependency> <!-- 引入zookeeper --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId> <artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId> <version>2.12.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId> <artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId> <version>2.12.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId> <artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId> <version>3.4.14</version> <!--排除这个slf4j-log4j12--> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> -
配置参数
server.port=8002 #当前应用名字 dubbo.application.name=consumer-server #注册中心地址 dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 -
本来正常步骤是需要将服务提供者的接口打包,然后用pom文件导入,我们这里使用简单的方式,直接将服务的接口拿过来,路径必须保证正确,即和服务提供者相同;
package ***.hwt.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public interface TicketService { public String getTicket(); } -
完善消费者的服务类
package ***.hwt.service; import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service//放到容器中 public class UserService { //拿到provider-service提供的票,要去注册中心拿到服务 @Reference//引用 pom坐标 可以定义路径相同的接口名 TicketService ticketService; public void buyTicket(){ String ticket = ticketService.getTicket(); System.out.println("在注册中心拿到:" + ticket); } } -
测试类编写
@SpringBootTest class ConsumerServiceApplicationTests { @Autowired UserService userService; @Test void contextLoads() { userService.buyTicket(); } } -
运行测试类拿到SpringBoot + Dubbo + zookeeper
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-AmLac0SU-1678702901823)(E:\笔记\typora-user-images\image-20230313175514593.png)]
upId>
zkclient
0.1
【新版的坑】zookeeper及其依赖包,解决日志冲突,还需要剔除日志依赖;
```java
<!-- 引入zookeeper -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId>
<version>2.12.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
<version>2.12.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId>
<artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId>
<version>3.4.14</version>
<!--排除这个slf4j-log4j12-->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
-
在springboot配置文件中配置dubbo相关属性!
#当前应用名字 dubbo.application.name=provider-server #注册中心地址 dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 #扫描指定包下服务 dubbo.scan.base-packages=***.hwt.service -
在service的实现类中配置服务注解,发布服务!注意导包问题,因为这里的Service注解需要导入的是dubbo中的注解,而不是spring的注解,所以要把其注入就要用***po***,不过最新版本的好像已经解决这个问题:一个新的注解@DubboService
@Service //将服务发布出去 @***ponent //放在容器中 public class TicketServiceImpl implements TicketService{ @Override public String getTicket() { return "SpringBoot + Dubbo + zookeeper"; } } -
测试运行,需要提前打开zookeepr服务
[外链图片转存中…(img-dNldBr94-1678702901822)]
-
可以看到服务已经存在了
逻辑理解 :应用启动起来,dubbo就会扫描指定的包下带有@***ponent注解的服务,将它发布在指定的注册中心中!
17.3、服务消费者
-
导入依赖,和之前的依赖一样;
<!--dubbo--> <!-- Dubbo Spring Boot Starter --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId> <artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.7.3</version> </dependency> <!--zookeeper--> <!-- https://mvnrepository.***/artifact/***.github.sgroschupf/zkclient --> <dependency> <groupId>***.github.sgroschupf</groupId> <artifactId>zkclient</artifactId> <version>0.1</version> </dependency> <!-- 引入zookeeper --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId> <artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId> <version>2.12.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId> <artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId> <version>2.12.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId> <artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId> <version>3.4.14</version> <!--排除这个slf4j-log4j12--> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> -
配置参数
server.port=8002 #当前应用名字 dubbo.application.name=consumer-server #注册中心地址 dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 -
本来正常步骤是需要将服务提供者的接口打包,然后用pom文件导入,我们这里使用简单的方式,直接将服务的接口拿过来,路径必须保证正确,即和服务提供者相同;
package ***.hwt.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public interface TicketService { public String getTicket(); } -
完善消费者的服务类
package ***.hwt.service; import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service//放到容器中 public class UserService { //拿到provider-service提供的票,要去注册中心拿到服务 @Reference//引用 pom坐标 可以定义路径相同的接口名 TicketService ticketService; public void buyTicket(){ String ticket = ticketService.getTicket(); System.out.println("在注册中心拿到:" + ticket); } } -
测试类编写
@SpringBootTest class ConsumerServiceApplicationTests { @Autowired UserService userService; @Test void contextLoads() { userService.buyTicket(); } } -
运行测试类拿到SpringBoot + Dubbo + zookeeper

